Cochliomyia hominivorax
New World screw-worm fly or screw-worm for short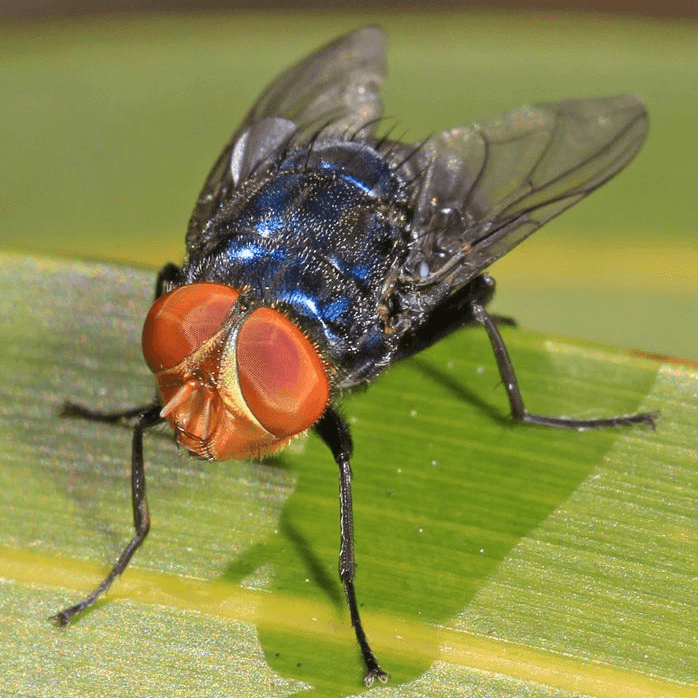
Cochliomyia hominivorax is a species of parasitic fly that is well known for the way in which its larvae (maggots) eat the living tissue of warm-blooded animals. It is present in the New World tropics. There are five species of Cochliomyia but only one species of screw-worm fly in the genus is parasitic; there is also a single Old World species in a different genus (Chrysomya bezziana). Infestation of a live vertebrate animal by a maggot is technically called myiasis. While the maggots of many fly species eat dead flesh, and may occasionally infest an old and putrid wound, screw-worm maggots are unusual because they attack healthy tissue.
Host Genome
Contig| Genome ID | Level | BUSCO Assessment |
|---|---|---|
| GCA_004302925.1 | Contig |
C:98.9%[S:95.2%,D:3.7%],F:0.8%,M:0.3%,n:1367
|
Download Genome Files
Related Symbionts
1 recordsSymbiont records associated with Cochliomyia hominivorax
Metagenome Information
0 recordsMetagenome sequencing data associated with Cochliomyia hominivorax
| Run | Platform | Location | Date | BioProject |
|---|---|---|---|---|
No metagenomes foundNo metagenome records associated with this host species. |
||||
Amplicon Information
0 recordsAmplicon sequencing data associated with Cochliomyia hominivorax
| Run | Classification | Platform | Location | Environment |
|---|---|---|---|---|
No amplicons foundNo amplicon records associated with this host species. |
||||
Related Articles
1 recordsResearch articles related to Cochliomyia hominivorax
| Title | Authors | Journal | Year | DOI |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Chan, XY; Hong, KW; Yin, WF; Chan, KG
|
SCIENTIFIC REPORTS
|
2016
|
10.1038/srep20016 |