Help
Get started with iSymBase
About iSymBase
iSymBase is a comprehensive database dedicated to insect symbionts research. It provides extensive resources including functional records, genomes, metagenomes, and research tools to empower scientific discovery and exploration.
Functional Records
Over 2,500 verified symbiont function records from scientific literature
Sequencing Data
Comprehensive collection of genomes, metagenomes, and amplicon data
Analysis Tools
Advanced tools for sequence analysis and symbiont identification
Quick Start Guide
Browse Database
Navigate through our comprehensive collection of symbiont records using the main navigation menu.
Search Records
Use our advanced search functionality to find specific symbiont records, genomes, or related data.
Analyze Data
Utilize our analysis tools for sequence alignment, symbiont identification, and more.
Data Modules
iSymBase provides six comprehensive data modules through the "Browser" menu, each offering specialized resources for insect symbiont research. These modules are designed to facilitate streamlined access to curated datasets and enable comprehensive exploration of insect-symbiont relationships.
Symbiont Record
Comprehensive data on insect symbiont records with verified symbiont functions from literature. Each entry includes key attributes such as symbiont name, host, functional description, function tags, and publication year.
Detailed reports contain taxonomic ranks, localization, transmission mode, supporting references, and related genomic data with direct links to literature sources providing experimental evidence.
Insect Host
Organizes insect species that harbor symbionts in a phylogenetic tree structure. Each host page provides integrated information including taxonomic classification, core microbiome composition, and related symbiont records.
Includes genome sequences and annotation files of insect hosts to facilitate metagenome dereplication and horizontal gene transfer (HGT) analysis.
Metagenome
Compiles metagenomes from symbiont-associated microbial communities with detailed information including accession numbers, sequencing platforms, locations, host information, and collection data.
Features hierarchical interactive pie charts for taxonomic composition visualization and provides downloadable analytical outputs including classification reports, assembled contigs, gene sequences, and compressed metagenome bins.
Amplicon
Compiles amplicon sequencing data from microbial communities associated with insect symbionts. Detailed pages include general sequencing information, taxonomic classification, geographic information, and functional annotation.
Provides hierarchical interactive visualizations for microbial diversity representation and downloadable outputs including classification reports, OTU sequences, raw sequencing files, and functional annotation reports.
Genome Catalog
Contains annotated genome sequences of insect symbionts from three primary sources: symbiont-related literature, public databases, and metagenome-assembled genomes (MAGs) obtained from binning.
Detailed pages include host species information, genome source, reference information, quality evaluation reports, and symbiont taxonomic classification.
Gene Catalog
Features annotated gene sequences from insect symbionts with detailed information on gene function, sequence data, GO annotation, KEGG pathway, and Pfam domains.
Includes advanced search functionality and word cloud visualization. Genes are clustered and dereplicated for each host species to eliminate redundancy and ensure data quality.
Enhanced Navigation Features
- • Cross-dataset navigation through keyword selection
- • Auto-suggest search functionality for quick entry discovery
- • Interactive navigation bars on detailed pages for seamless section switching
Browse Guide
iSymBase provides comprehensive access to various types of data related to insect symbionts. This guide will help you navigate through our data browsing interfaces and make the most of our search capabilities.
Quick Tip
Use the navigation menu on the left to quickly jump to different sections of this guide. Each section provides detailed information about specific data types and search features.
1. Home
The home page provides an overview of the database content and quick access to main features.
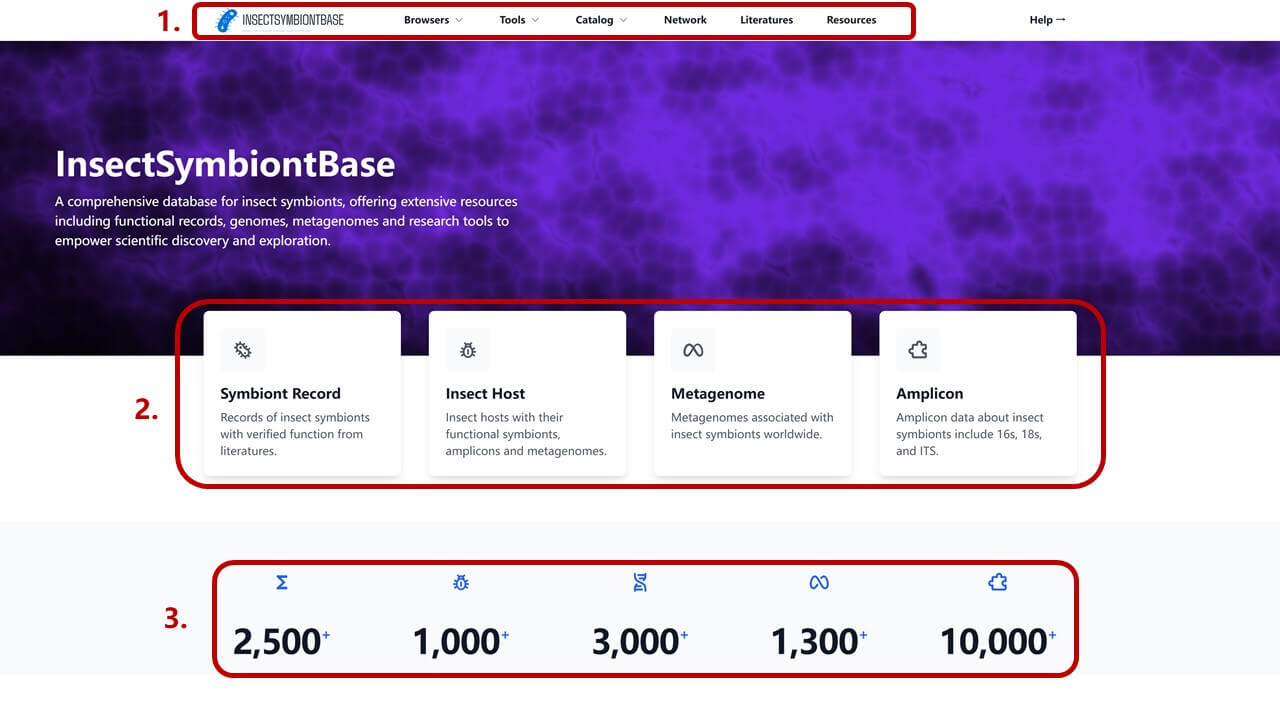
The home page consists of three main sections:
- Main Navigation Bar: Access to different data browsing interfaces and tools
- Quick Access Cards: Direct links to major data categories including Symbiont Records, Insect Hosts, Metagenome, and Amplicon data
- Database Statistics: Overview of current data volume in the database, click number to browse the specific page
2. Symbiont Record
Browse and search through our comprehensive collection of symbiont records.
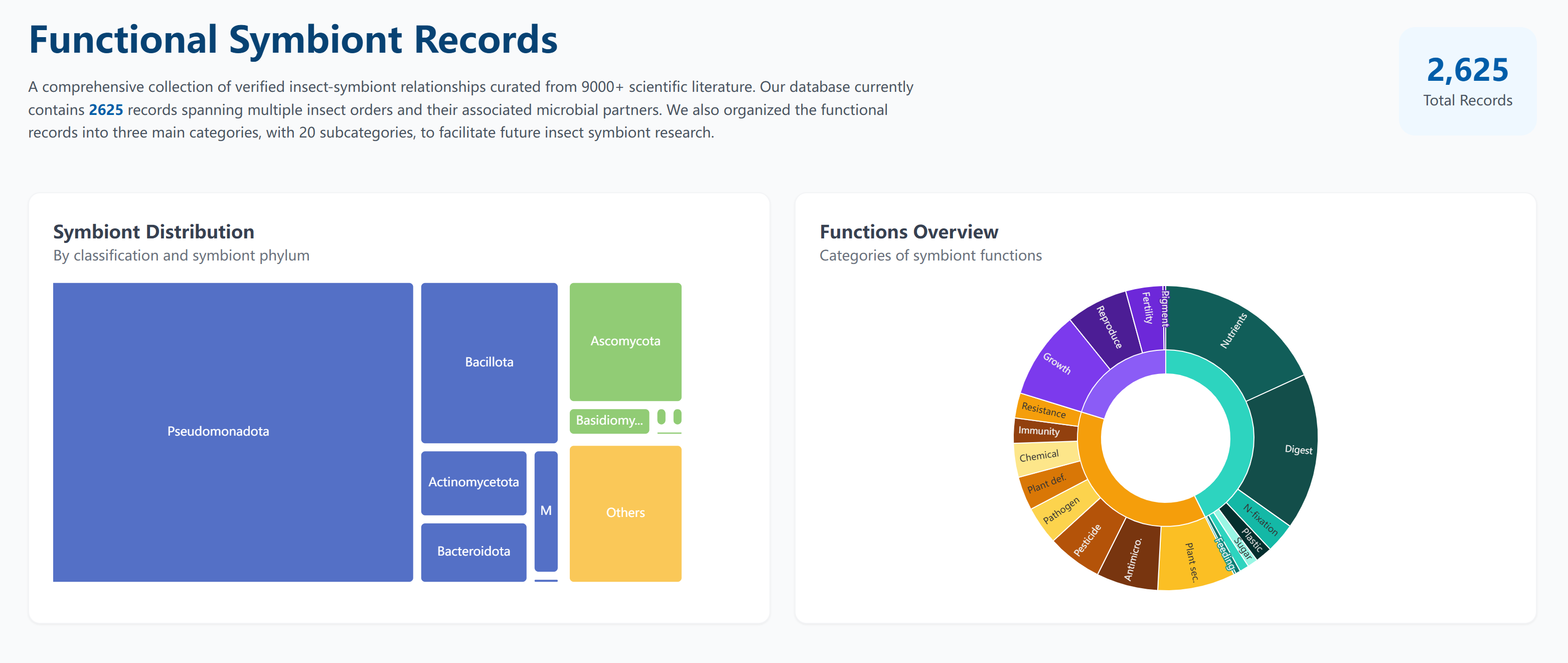
The Symbiont Record page provides an overview of:
- Total number of symbiont records from literatures in the database
- Distribution of symbiont records across different phylums
- View the classification of Function Tags and the number of Symbiont Records
2.1 Symbiont Records Table
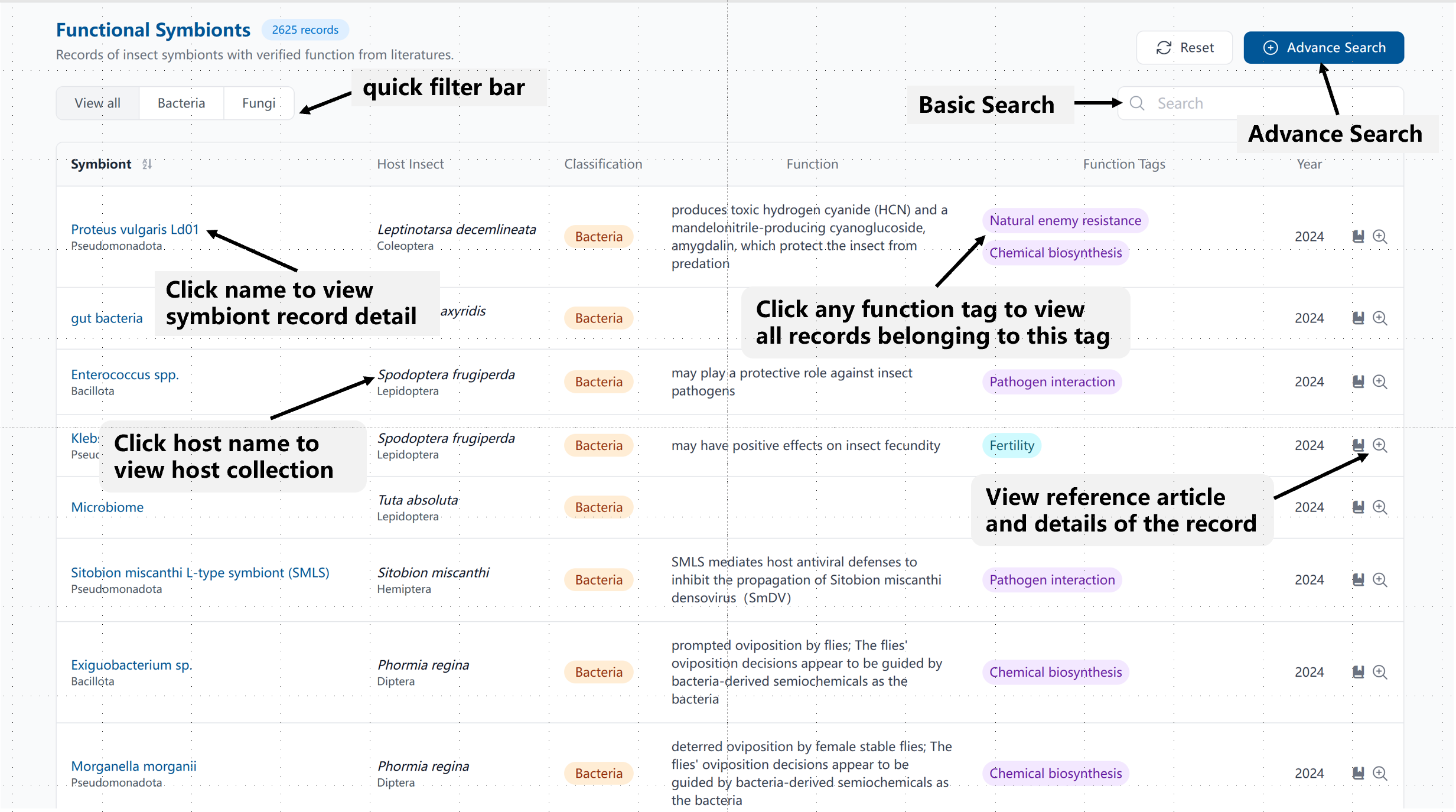
The Function Symbionts Table provides an intuitive interface for exploring symbiont records. You can filter by symbiont type, view detailed record information, and explore tags, hosts, and references.
View detailed guidance through images and on-page guidelines.
2.2 Symbiont Search
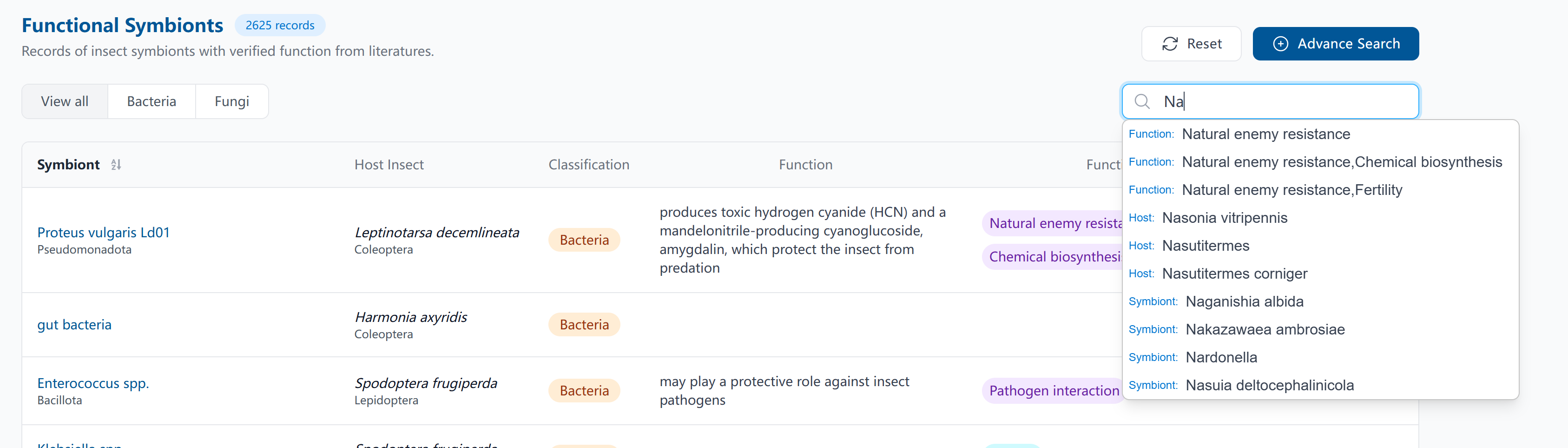
You can easily find any symbiont record of interest using the basic search, which allows queries across multiple fields such as symbiont name, host, function, and associated tags. Additionally, the search feature includes helpful tools like autocompletion and associative suggestions to streamline your exploration.
You can also use the advanced search to customize multi-field filters and retrieve records that match your specific interests.
2.3 Symbiont Detail
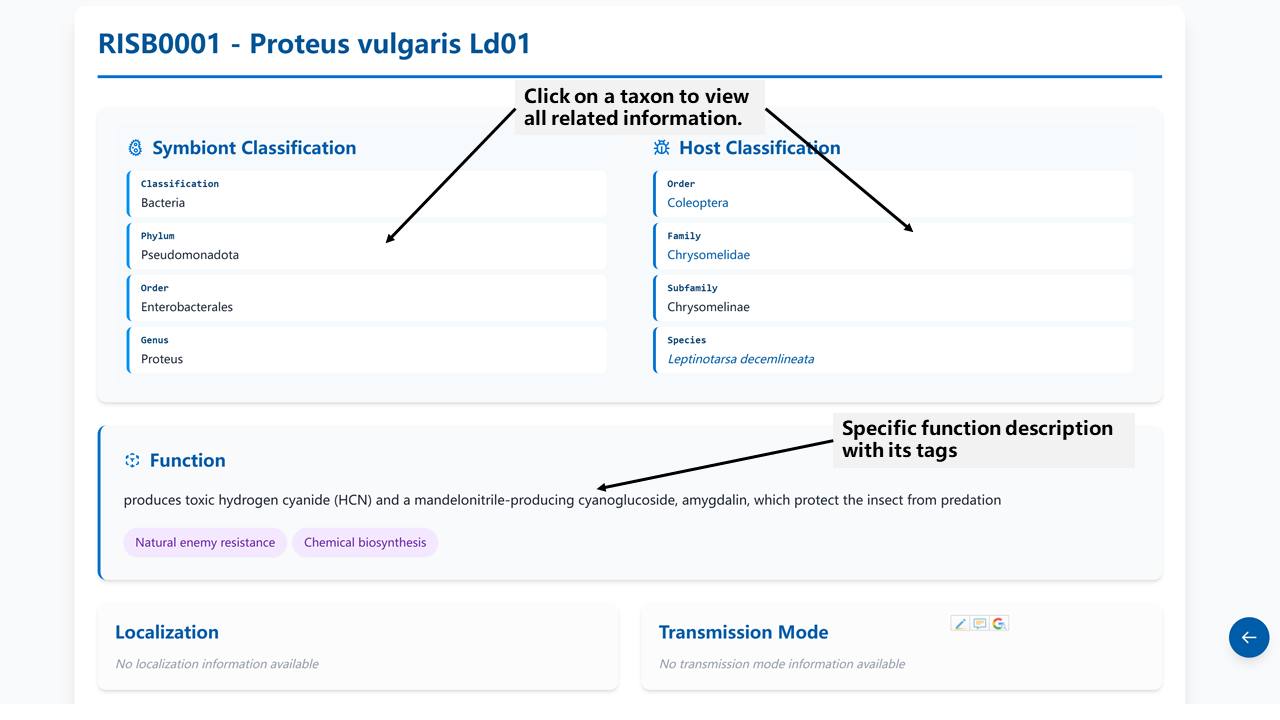
The Symbiont Detail page displays comprehensive information about a specific symbiont record, including:
- Basic taxonomic classification (Click each taxon to view all related information)
- Detailed functions with tags are manually extracted and curated from the original article
- Localization and transmission mode are provided if included in the reference article
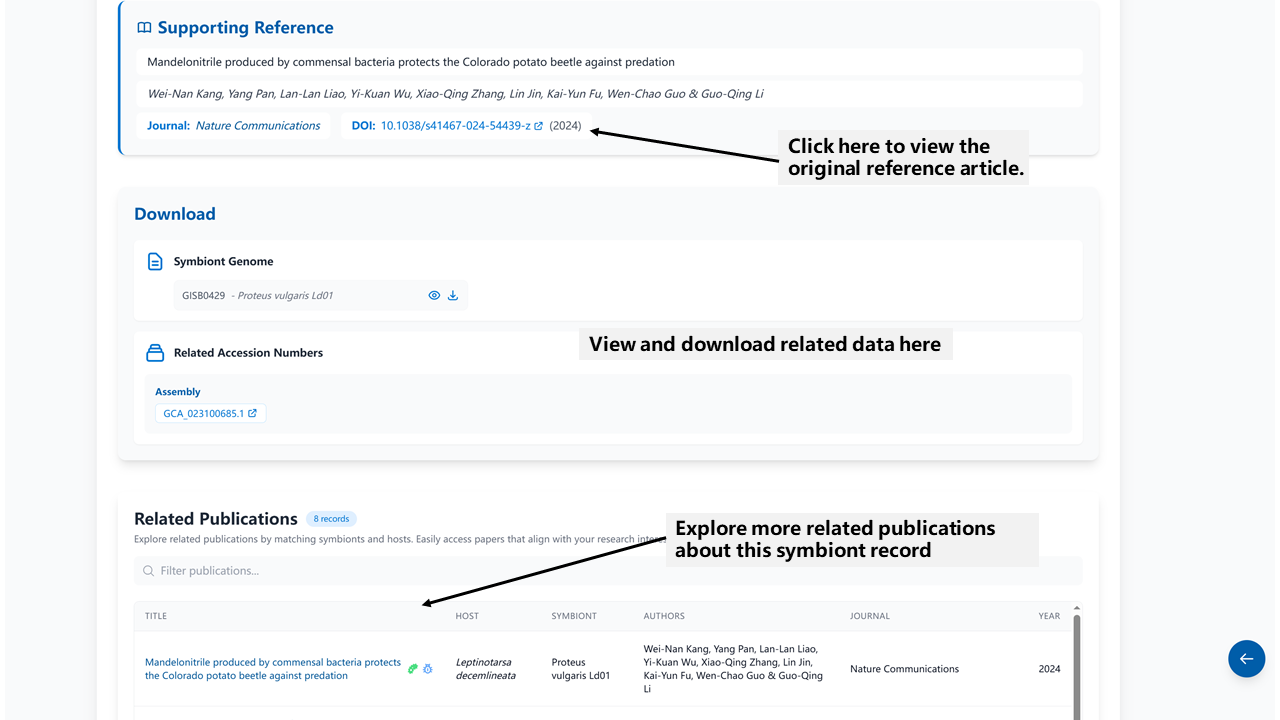
- Supporting Reference for this record including the authors, journal and the link to original article
- Download: Curated symbiont genomes and other related data links, including 16S sequences, amplicons, and metagenomes etc
- Other publications related to the symbiont and host associated with this record
3. Insect Host
Explore information about insect hosts and their associated symbionts.
3.1 Host Tree
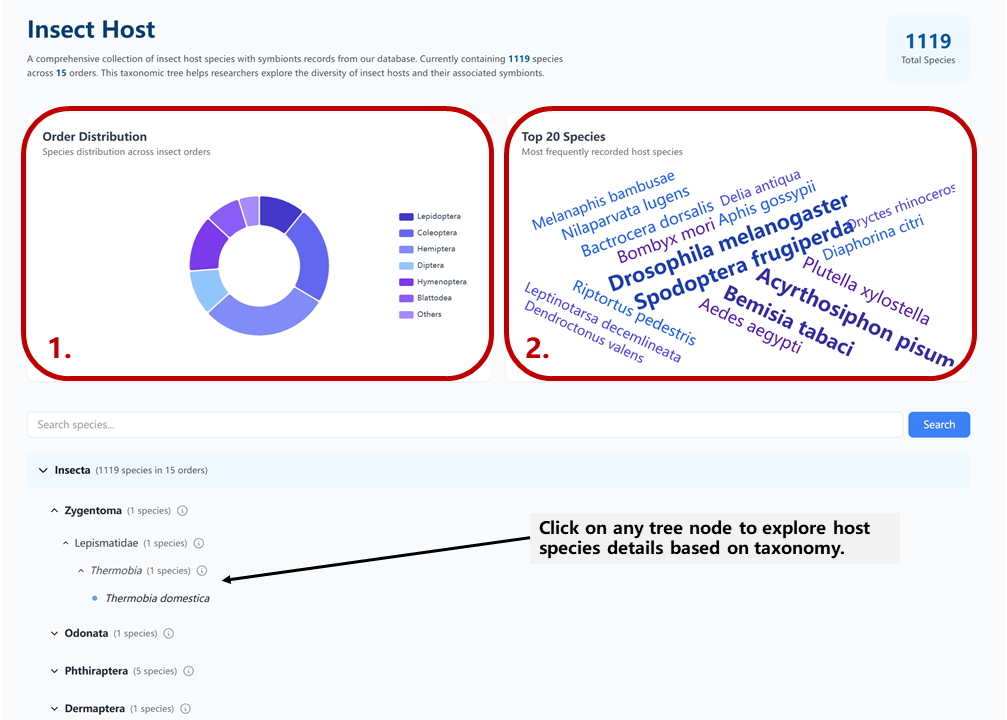
The Host Tree page provides a comprehensive visualization of insect hosts in our database:
- 1. The left panel shows the total number of host records and their distribution across different orders
- 2. The right panel displays the most frequently recorded host species, which can be directly searched by click
The interactive taxonomic tree allows you to:
- Navigate through different taxonomic levels from order to species
- Click on any node to view detailed information about that taxonomic group
- See the number of symbiont records associated with each host group
3.2 Host Detail
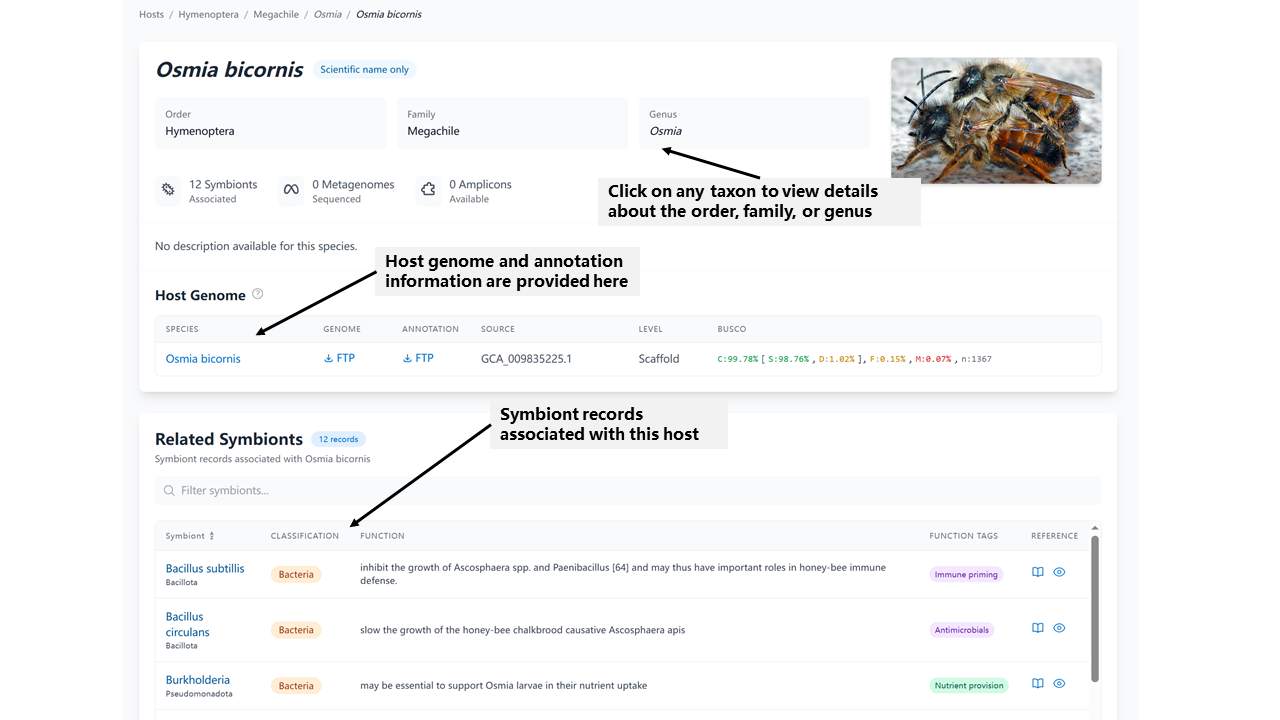
The Host Detail page provides comprehensive information about a specific insect host and its associated symbionts:
- Host Information: Complete taxonomic classification and basic information about the host species
- Associated Symbionts: List of all symbionts recorded for this host, including their functions and relationships. Click to see records detail
- Sequence Data: Available metagenome and amplicon data associated with this host (Figure not show)
- Literature References: Publications documenting this host with its symbionts
Core Microbiome Composition
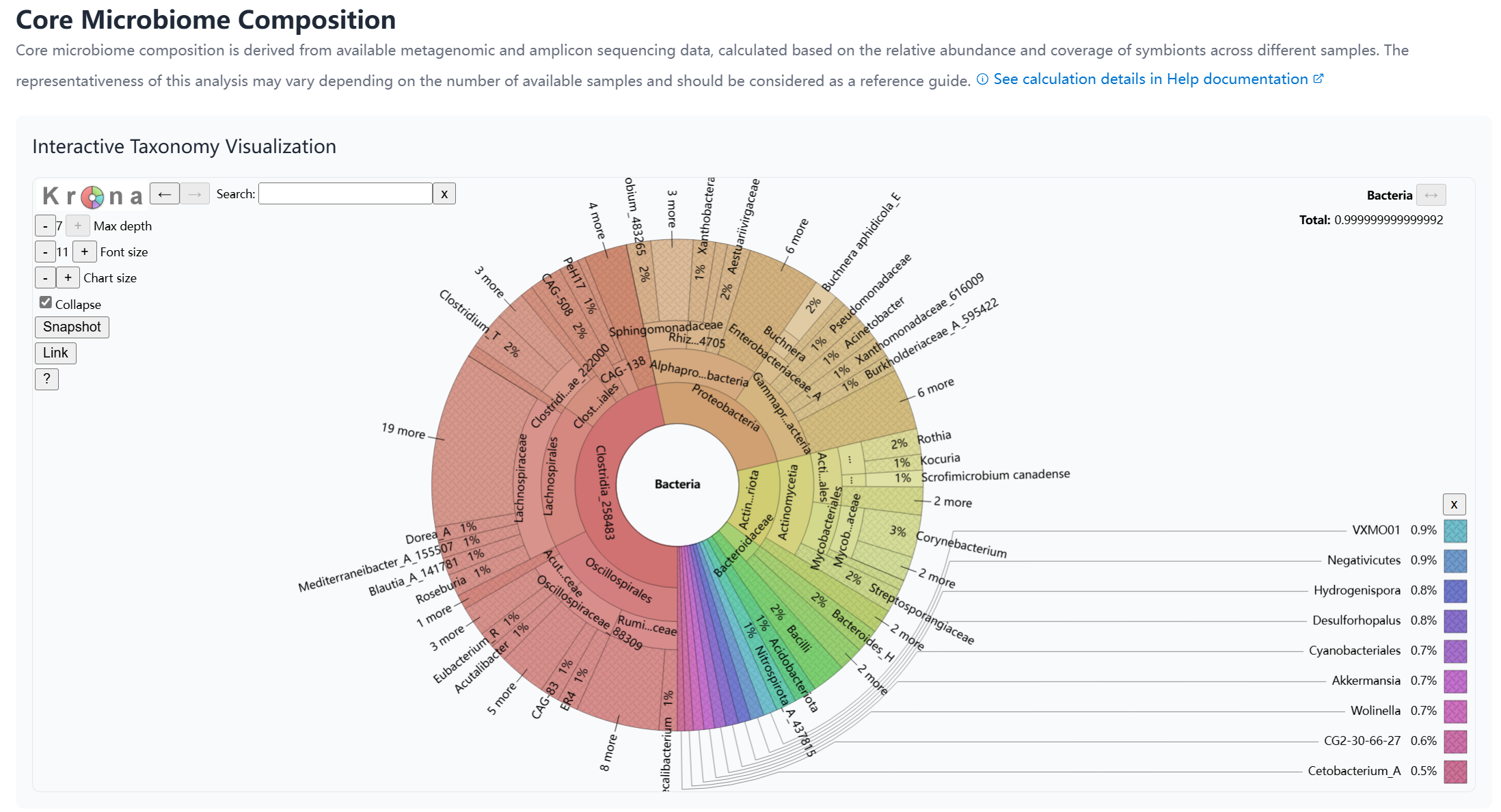
The Core Microbiome Analysis provides insights into the consistent microbial associations within insect species. This analysis is performed on species with substantial sample coverage (>10 amplicon samples).
Analysis Methodology
Core symbionts are identified using multiple metrics:
- Mean abundance across samples
- Standard deviation of abundance
- Coefficient of variation (CV)
- Sample coverage
Representative Abundance Formula
Representative abundance = mean abundance + coverage + (2 - CV)
Note: Values are normalized to reflect relative importance
Quality Control
To ensure data quality, we apply the following filters:
- Exclude species with CV > 2
- Remove symbionts found in only one sample
- Require minimum of 10 amplicon samples per host species
Usage Tips
- Use the visualization to explore core microbiome patterns
- Compare core microbiomes across different host species
- Consider sample coverage when interpreting results
- Reference literature-validated examples for context
4. Metagenome
The Metagenome section compiles comprehensive metagenomic data from symbiont-associated microbial communities, providing both raw data and detailed analysis results from January 2008 to July 2024.
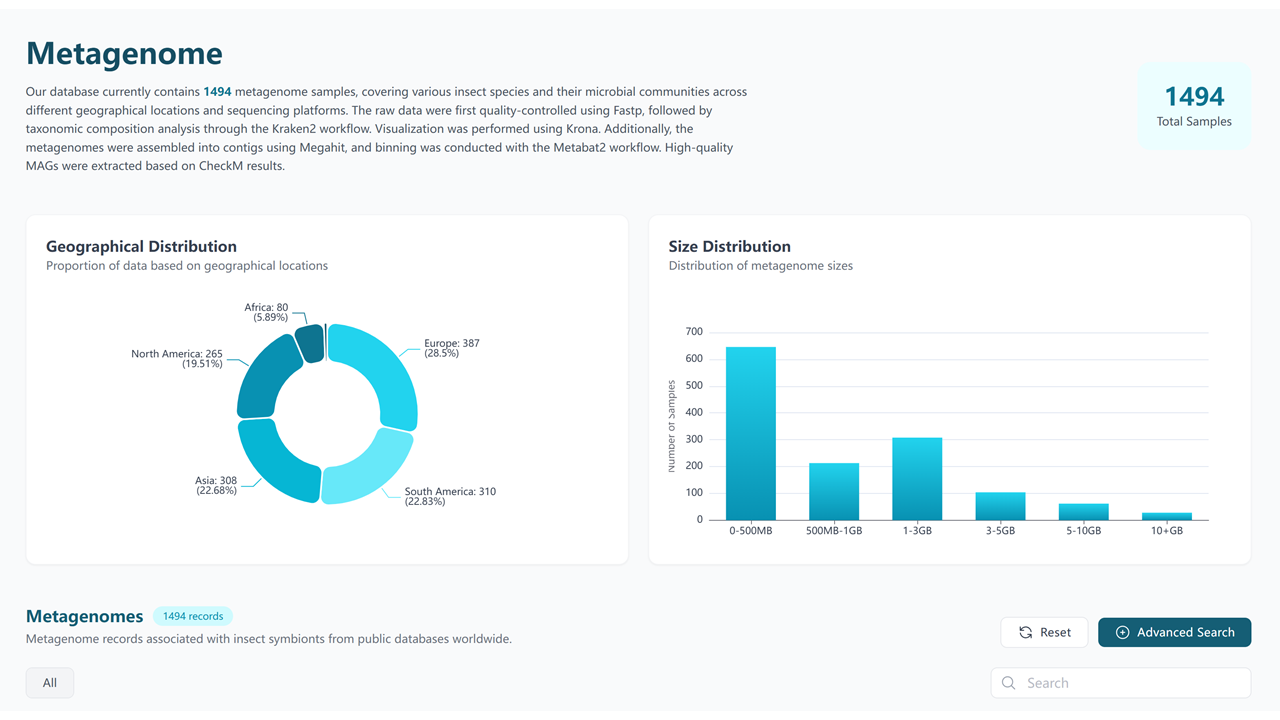
Our metagenome data is sourced from:
- NCBI SRA database
- NGDC database
- EBI database
- Published literature on insect symbionts
Analysis Pipeline
- Quality control: Fastp (v0.23.4)
- Taxonomic profiling: Kraken2 (v2.1.3)
- Assembly: Megahit (k-min 27, k-max 127)
- Binning: MetaBAT2 (v2.17)
- Quality assessment: CheckM (v2.17)
4.1 Metagenome Table
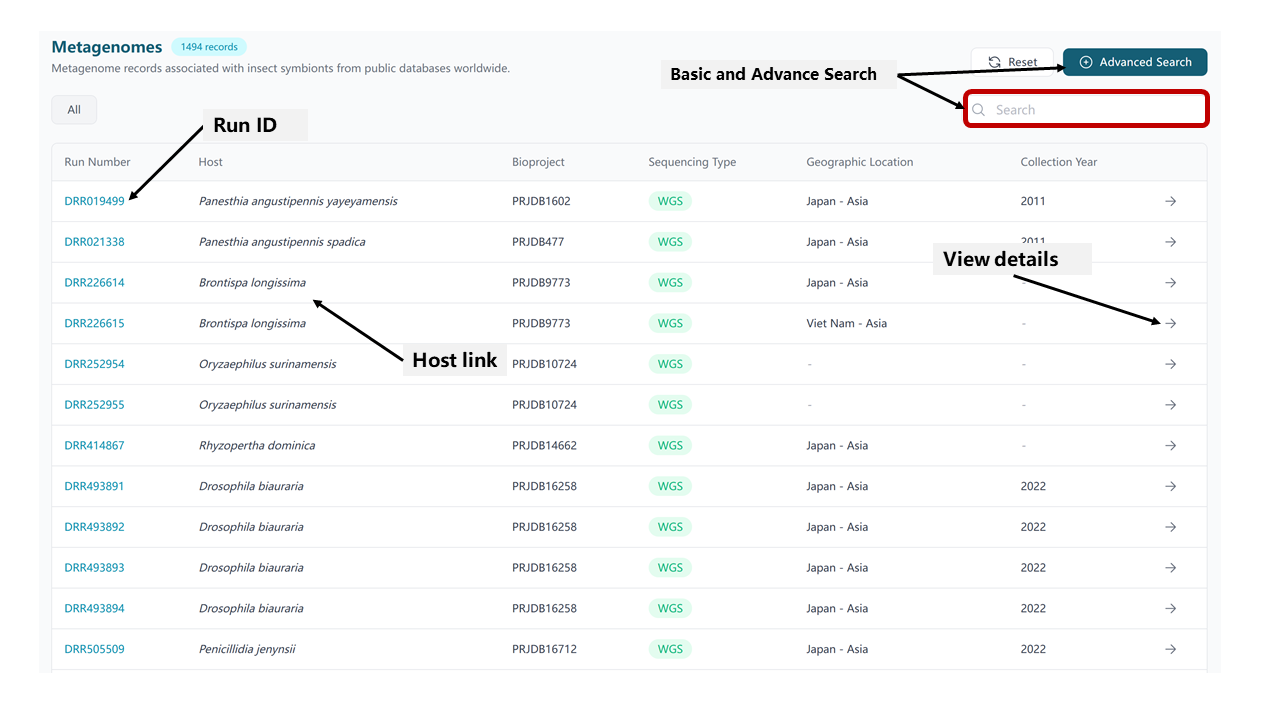
The Metagenome Table provides a comprehensive overview of all metagenomic samples, including key metadata and analysis results.
Available Information
- Basic Metadata:
- Accession numbers
- Sequencing platform
- Geographic location
- Collection date
- Data size
- Host Information: Detailed taxonomic and biological information about the insect host
- Quality Metrics: Results from quality control analysis
4.2 Metagenome Details
Basic Information

The basic information section provides comprehensive metadata about the metagenome sample:
- Sample Information:
- Accession ID and BioProject
- Collection date and location
- Sequencing platform and strategy
- Data size and quality metrics
- Host Details:
- Host species and taxonomy
- Sampling tissue or body part
- Development stage
Taxonomic Classification
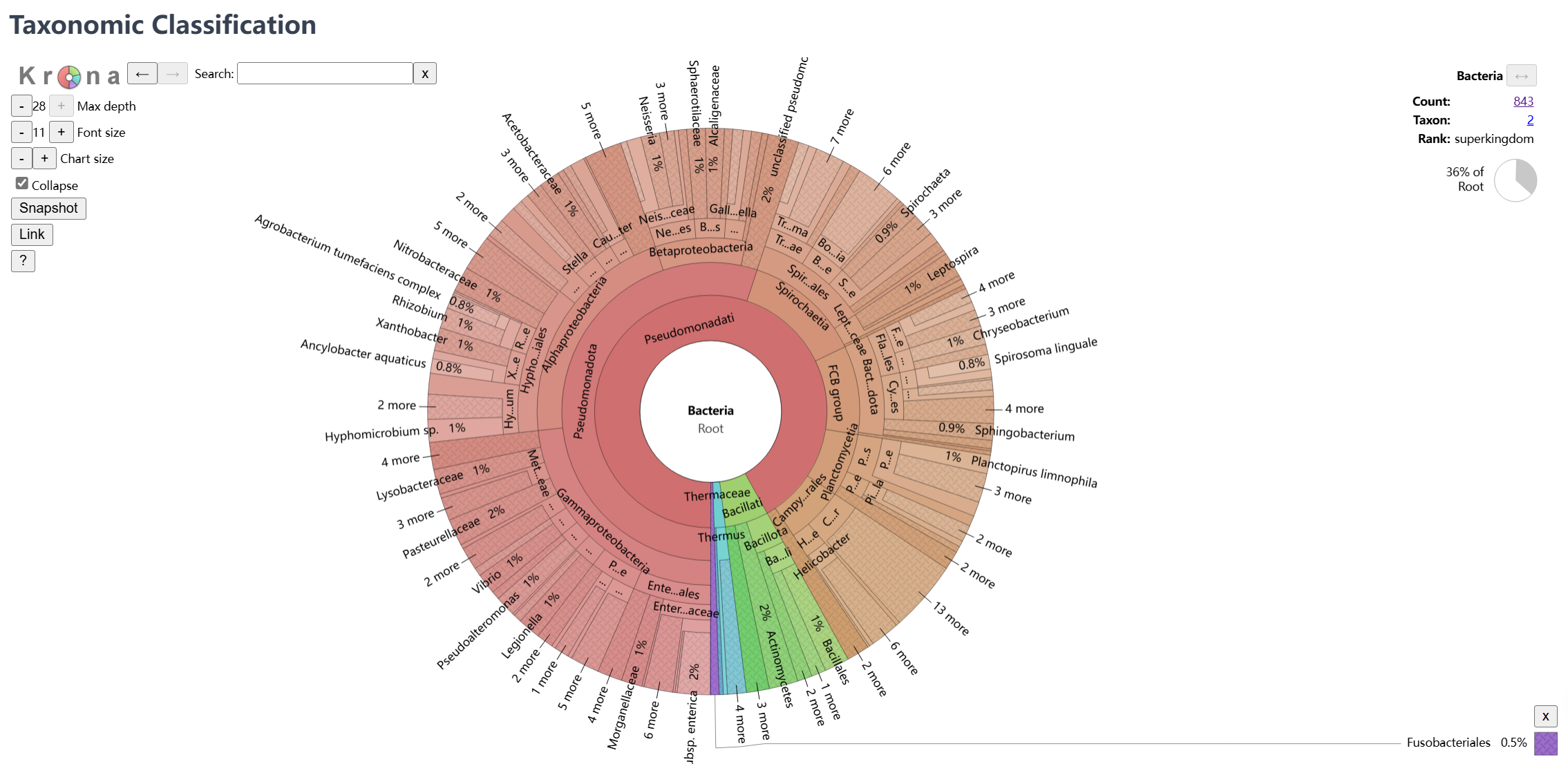
Interactive visualization of the community taxonomic composition:
- Krona Chart:
- Hierarchical interactive pie chart
- Drill-down exploration of taxonomic levels
- Percentage abundance display
- Export options for visualization
- Classification Details:
- Kingdom to species level classification
- Relative abundance information
- Read count statistics
Potential Symbionts
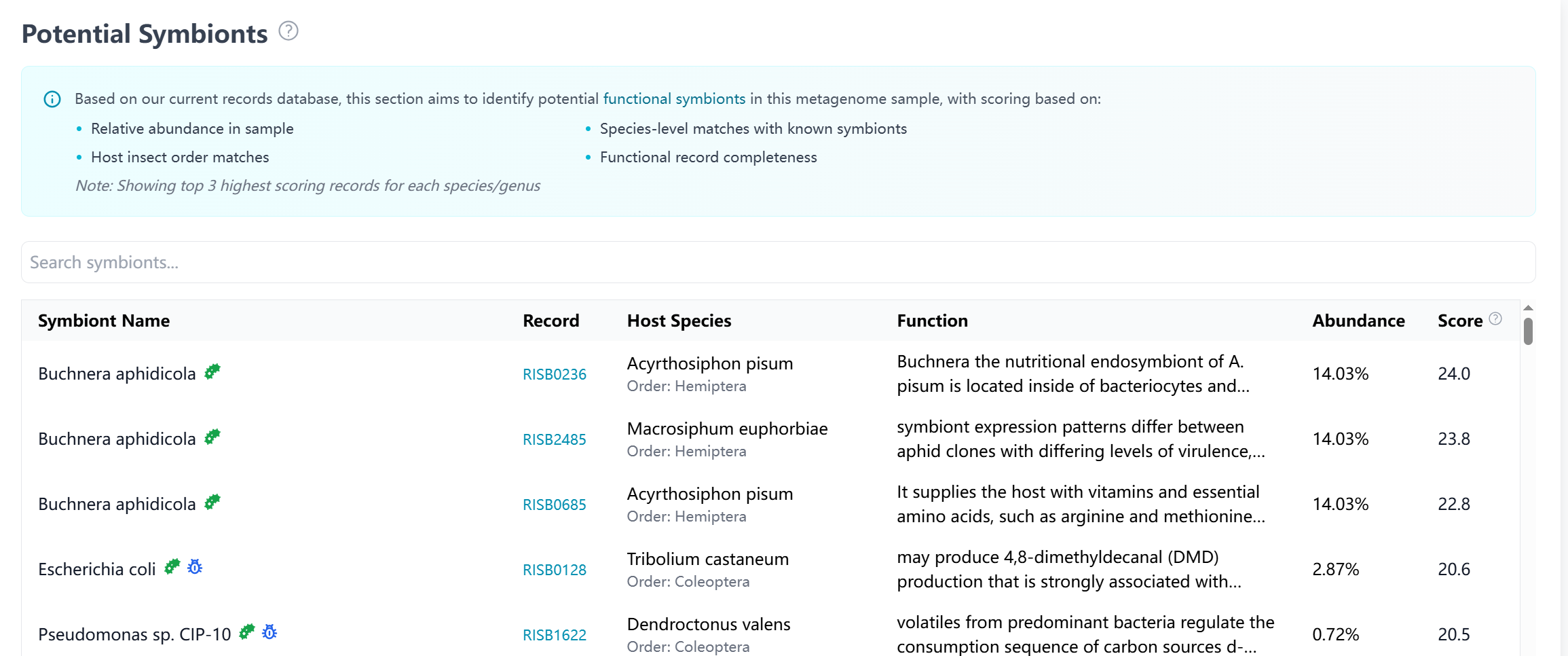
Analysis of potential symbiotic microorganisms identified in the sample:
- Symbiont Identification:
- Known insect symbionts detected
- Abundance levels and distribution
- Links to related symbiont records
Download Section
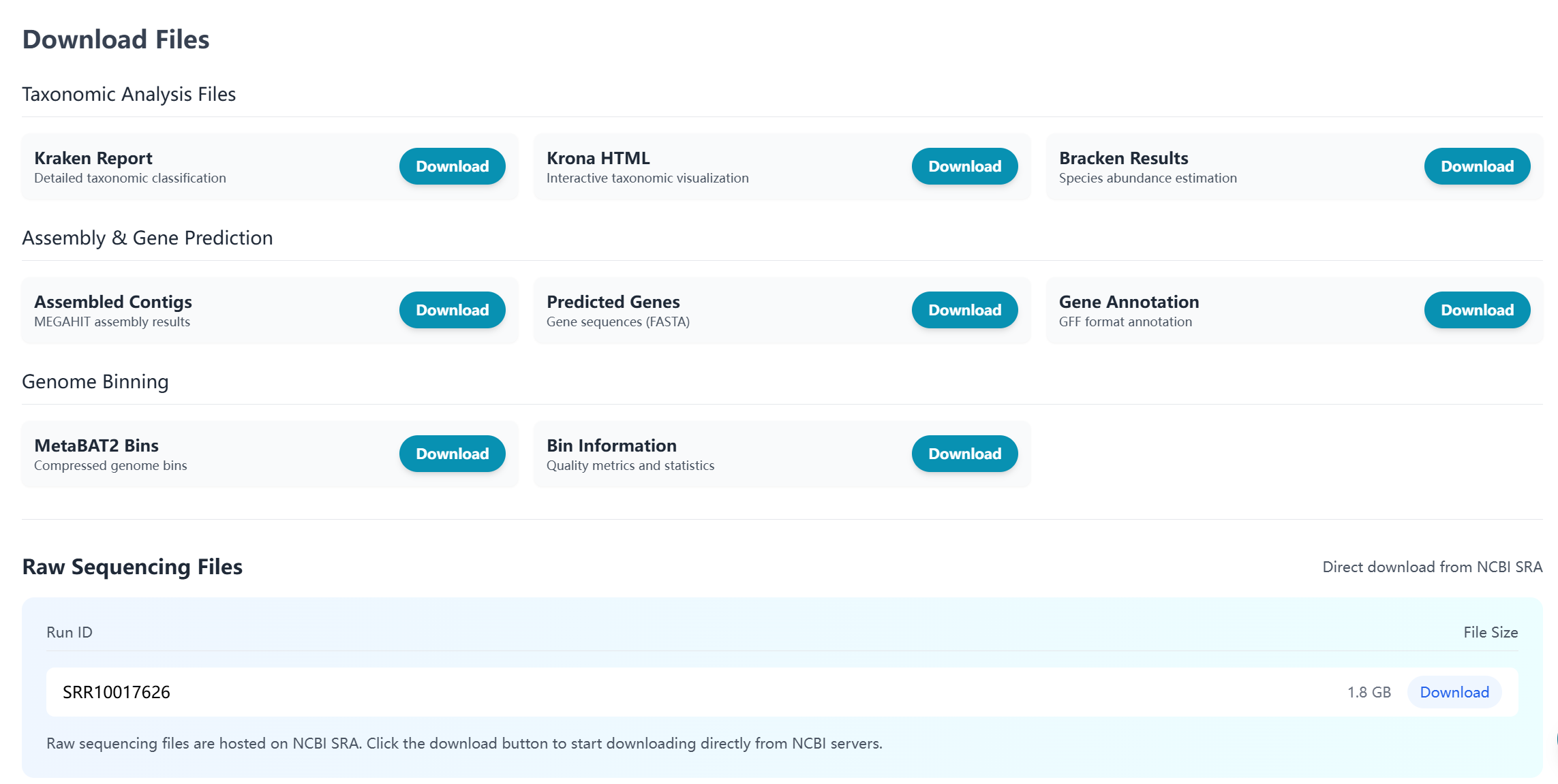
Comprehensive data download options for further analysis:
- Raw Data:
- Original sequencing reads (FASTQ)
- Quality control reports
- Processed Results:
- Taxonomic classification reports
- Assembled contigs (FASTA)
- Gene predictions and annotations
- MAG sequences and quality reports
- Visualization Files:
- Krona chart HTML files
- Summary statistics and plots
5. Amplicon
Our database features a comprehensive collection of 16S amplicon sequencing data from insect-associated microbial communities, with over 12,410 samples representing diverse insect species across multiple geographical regions.
Analysis Pipeline
- Quality control and merging: Fastp (v0.23.4)
- Primer trimming: Seqtk (v1.4)
- OTU clustering: Vsearch (v2.28.1)
- Taxonomy classification: QIIME2 (v2024.2.0)
- Functional prediction: FAPROTAX (v1.2.10)
5.1 Amplicon Analysis
Taxonomy Annotation
Our standardized taxonomy annotation workflow includes:
- Data Preprocessing:
- Quality control and paired-end merging
- Primer sequence removal
- Standardized 5' end trimming (20 bp)
- OTU Generation:
- Sequence deduplication (minimum frequency: 3)
- 97% similarity clustering
- De novo chimera removal
- Taxonomic Classification:
- QIIME2 with Greengenes classifier
- Vsearch SINTAX algorithm
- Interactive Krona visualization
Functional Prediction
FAPROTAX-based functional analysis of microbial communities:
- Prediction Process:
- Mapping taxonomic data to functional pathways
- Based on QIIME2 classification results
- Utilizing FAPROTAX database
- Output Files:
- Functional pathway summaries
- Detailed FAPROTAX reports
- Metabolic function predictions
Download Section
Available data files for download:
- Raw Data:
- Original FASTQ files
- Quality control reports
- Analysis Results:
- OTU tables and sequences
- Taxonomy classification results
- Functional prediction reports
Analysis Tools Guide
iSymBase provides a suite of powerful analysis tools to help researchers explore and analyze insect symbiont data. This guide will help you understand and effectively use each tool.
Quick Tip
Each tool is designed for specific analysis needs. Use the navigation menu on the left to jump to detailed instructions for each tool.
1. BLAST
BLAST (Basic Local Alignment Search Tool) is a powerful tool for comparing query sequences against our database of insect symbiont sequences. iSymBase provides specialized BLAST functionality supporting various sequence types for comprehensive similarity analysis.
1.1 Search Interface
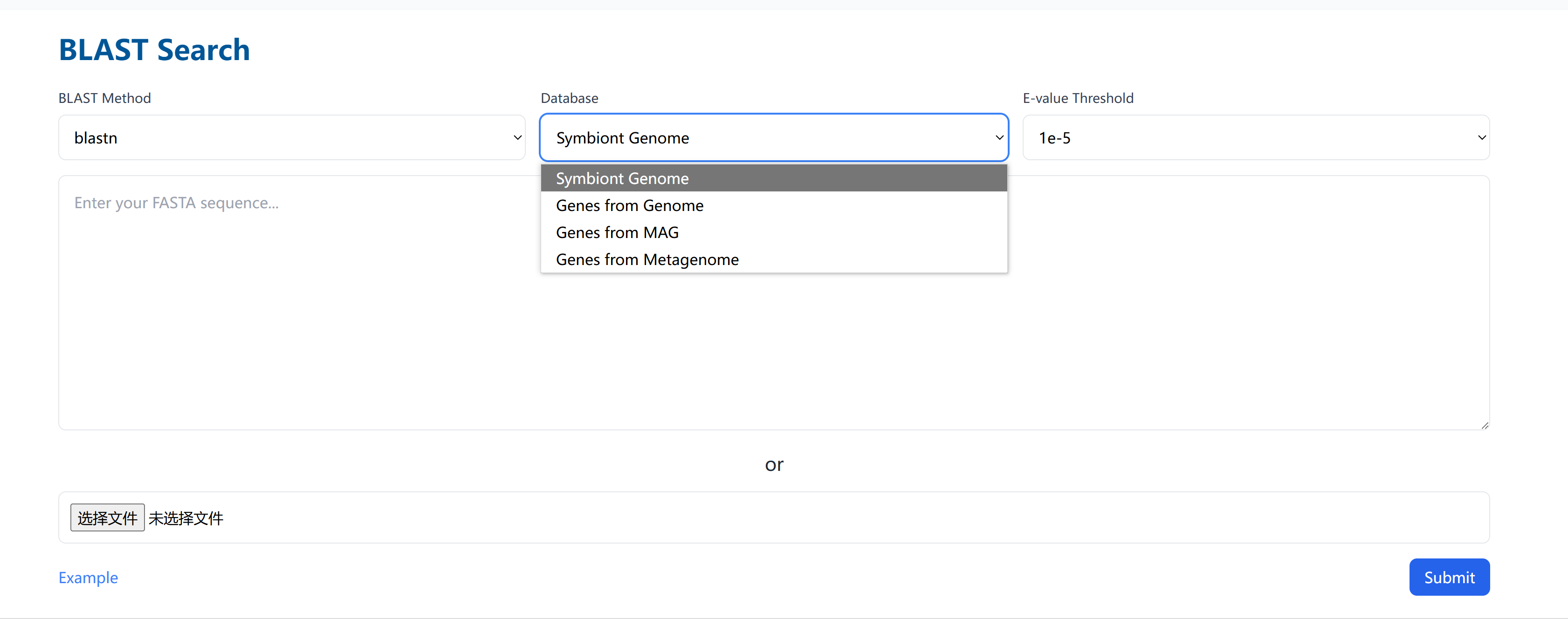
Key Components:
1. BLAST Configuration
BLAST Method
- blastn - For nucleotide sequence alignment
- tblastn - For protein query against nucleotide database
Database Options
- Symbiont Genome Database
- Genome-derived Genes
- MAG-derived Genes
- Metagenome-derived Genes
E-value Settings
- 1e-5 (Default) - High stringency search
- 1e-3 - Medium stringency search
- 1e-1 - Low stringency search
2. Sequence Input Options
Direct Text Input
- Paste FASTA sequence directly
- Load example sequences for practice
- Best for single or short sequences
File Upload
- Compatible with .fasta and .txt files
- Maximum file size: 10MB
- Recommended for multiple or long sequences
💡 Quick Tips
- Ensure your sequence is in proper FASTA format
- Start with default E-value for best results
- Use example sequences to learn the interface
1.2 Results Interpretation
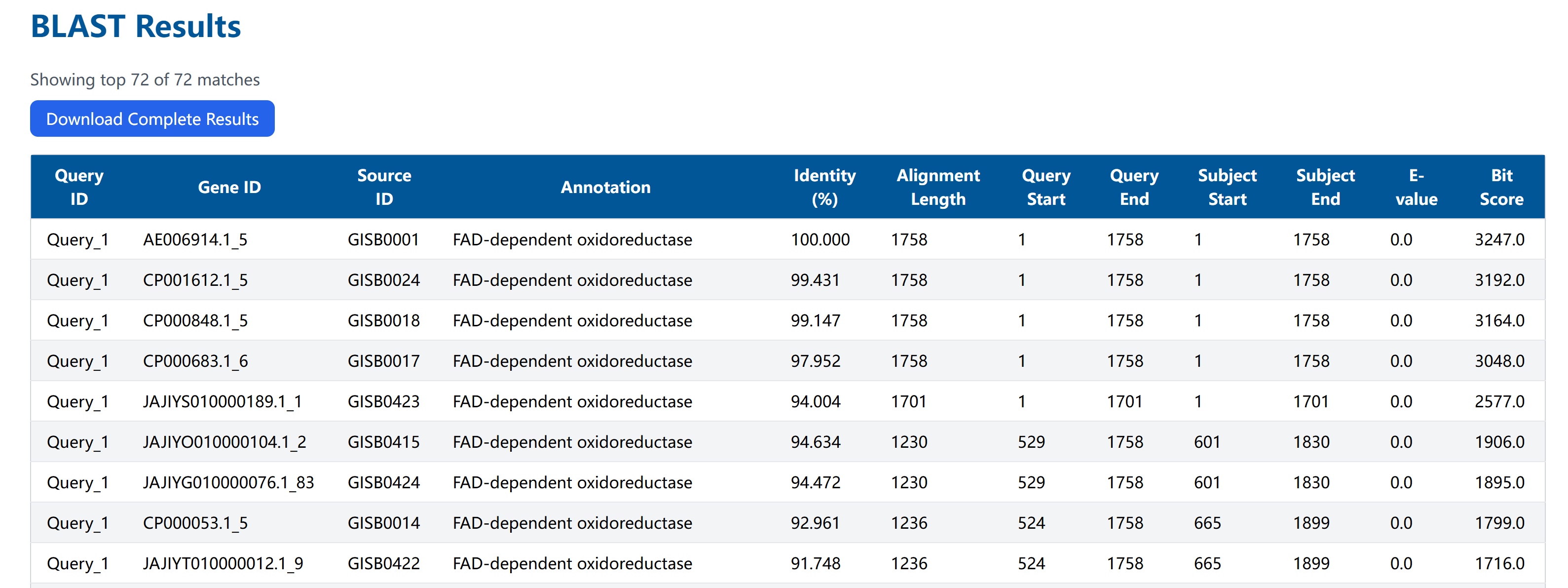
Understanding Results
Basic Information
- Query ID: Query sequence identifier
- Subject Name/ID: Target sequence information
- Identity (%): Sequence similarity
- Alignment Length: Match length
Position & Scores
- Query/Subject Start/End: Alignment positions
- E-value: Expected value (lower is better)
- Bit Score: Normalized score
Usage Tips
- Start with strict E-value and adjust as needed
- Use file upload for long sequences
- Try example sequences to familiarize yourself
- Verify sequence format correctness
2. Batch Anno
The Batch Anno tool helps you identify potential symbionts from taxonomic composition data of your samples. This powerful tool supports multiple input formats and provides comprehensive analysis of symbiont-host relationships.
Interface Overview

The Batch Anno interface consists of several key components:
- Input Methods: Choose between file upload or direct text input
- File Type Selection: Support for Kraken, MetaPhlAn, and Krona formats
- Host Information: Specify the insect host details
- Guide Section: Click highlight name to see detailed examples of supported input formats
Data Input Methods
1. File Upload

The file upload interface allows you to:
- Drag and drop files directly into the upload area
- Click to browse and select files from your computer
- View upload status and file information
- Supported formats: .txt, .tsv, .csv, .tab (max 10MB)
2. Text Input
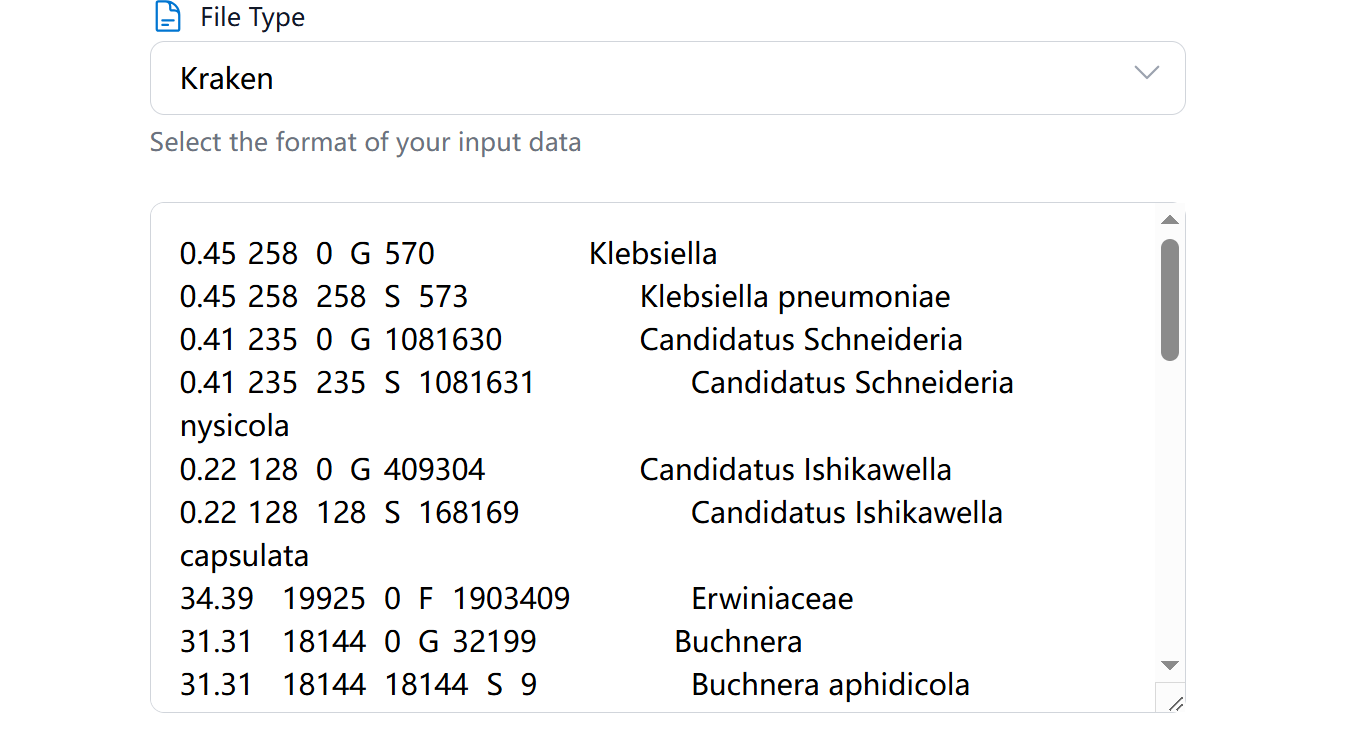
The text input option allows you to:
- Directly paste your taxonomic composition data
- Preview and edit data before submission
- Quickly test small datasets
3. File Format Example
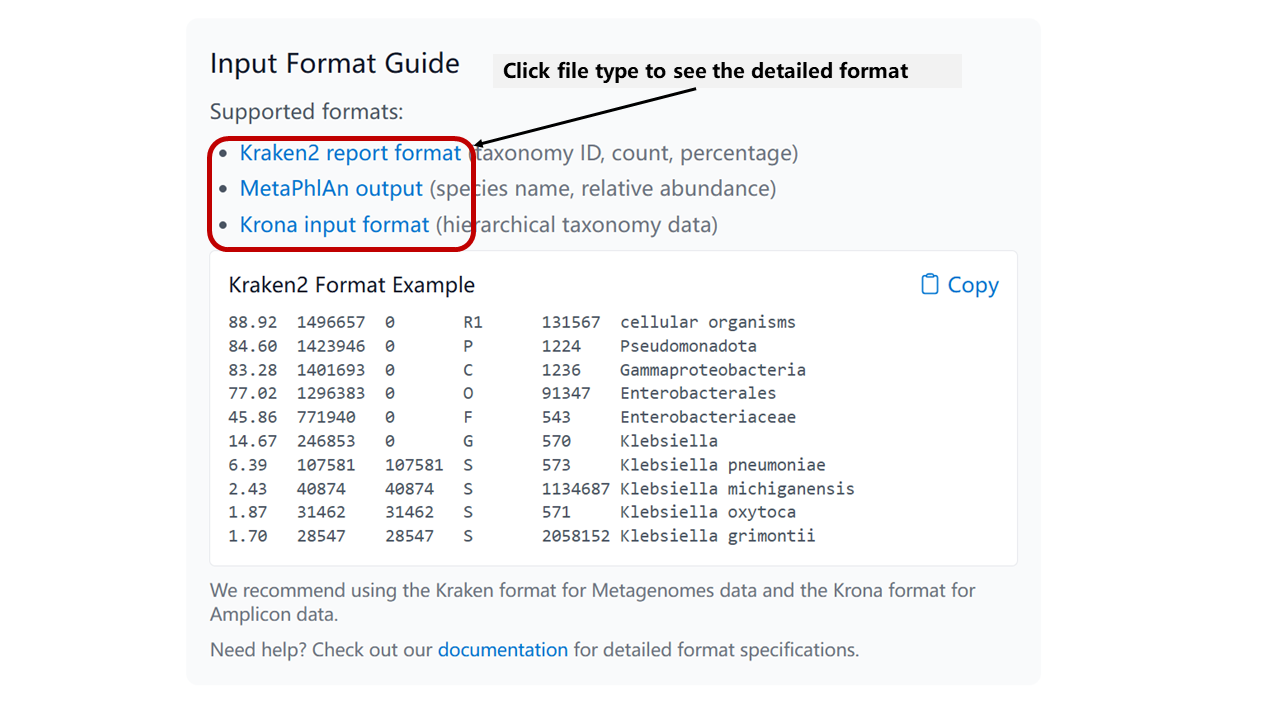
Here are some important reminders when preparing your files:
- Ensure Correct Name: Make sure your species or genus names are consistent with NCBI taxnomy
- Data Accuracy: Verify that the data in your files is accurate and properly formatted
- File Naming: Use clear and descriptive file names to avoid confusion
Host Information
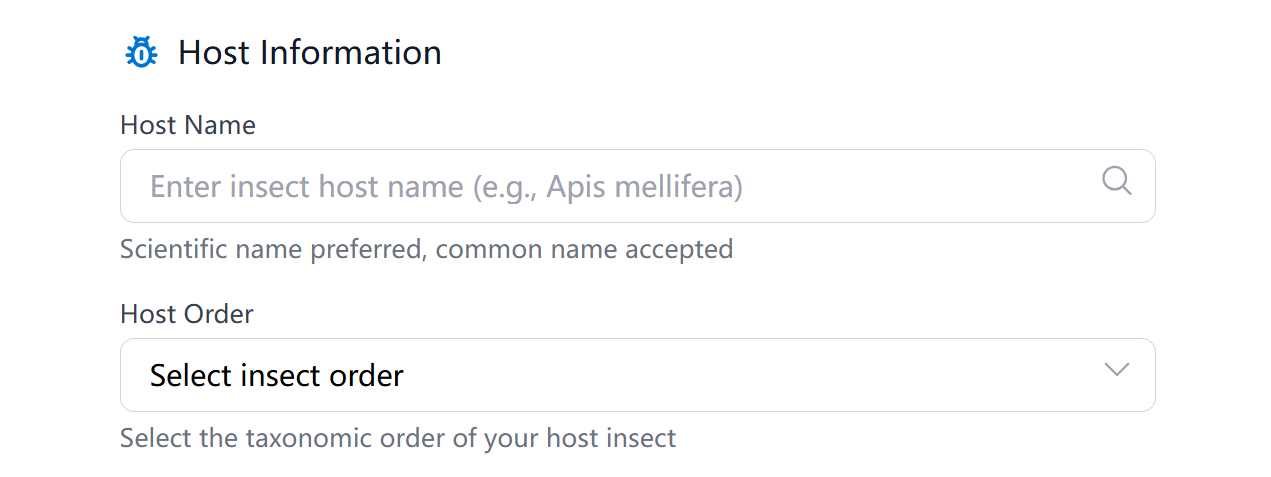
Provide accurate host information to improve search results:
- Host Name: Enter the scientific name or common name of your insect host
- Host Order: Select the taxonomic order from the dropdown menu
Understanding Results
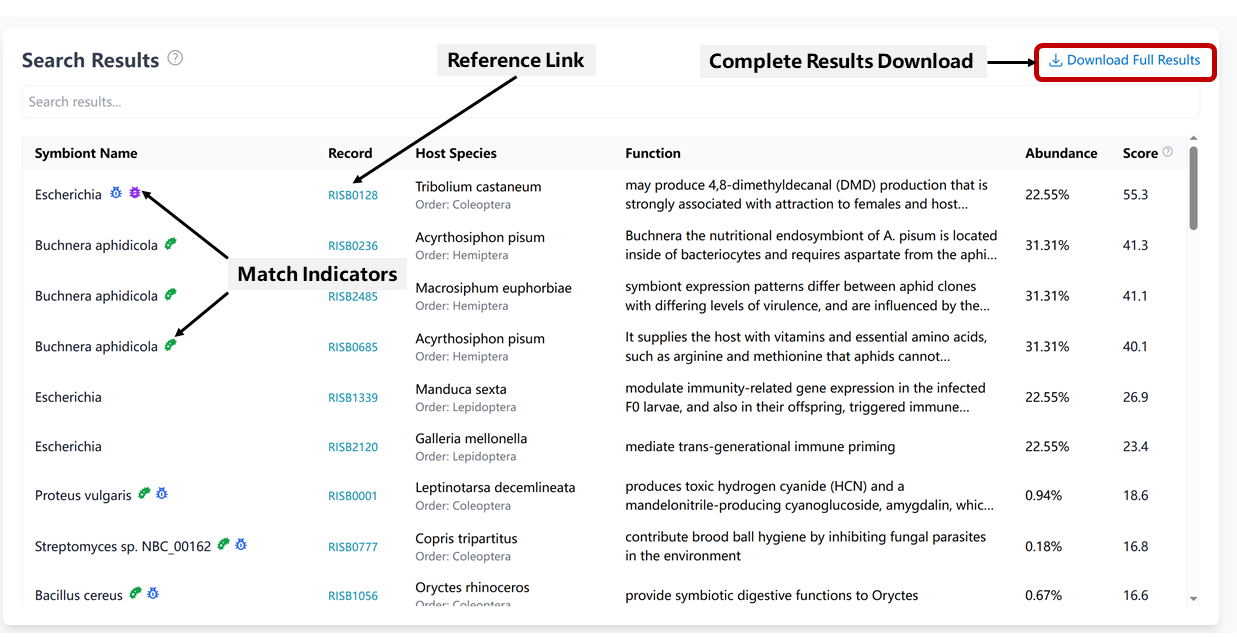
The results section provides comprehensive information about potential symbionts:
- Match Indicators:
- Species Match: Exact species-level match in database
- Host Order Match: Found in the same insect order
- Host Species Match: Found in the same host species
- Score Composition: Based on multiple factors including:
- Symbiont abundance in your sample
- Species match bonus
- Host match bonus
- Function richness
- Additional Features:
- Search within results
- Download complete results
- View detailed symbiont records
Tips and Best Practices
For Best Results:
- Provide accurate host taxonomic information
- Use standardized taxonomic names in your input data
- Check the format guide for proper data formatting
- Consider using Kraken format for metagenomes and Krona format for amplicon data
3. Interactive Map
The Interactive Map provides a geographical visualization of insect symbiont samples worldwide, allowing you to explore the spatial distribution of different types of sequencing data.
Map Overview
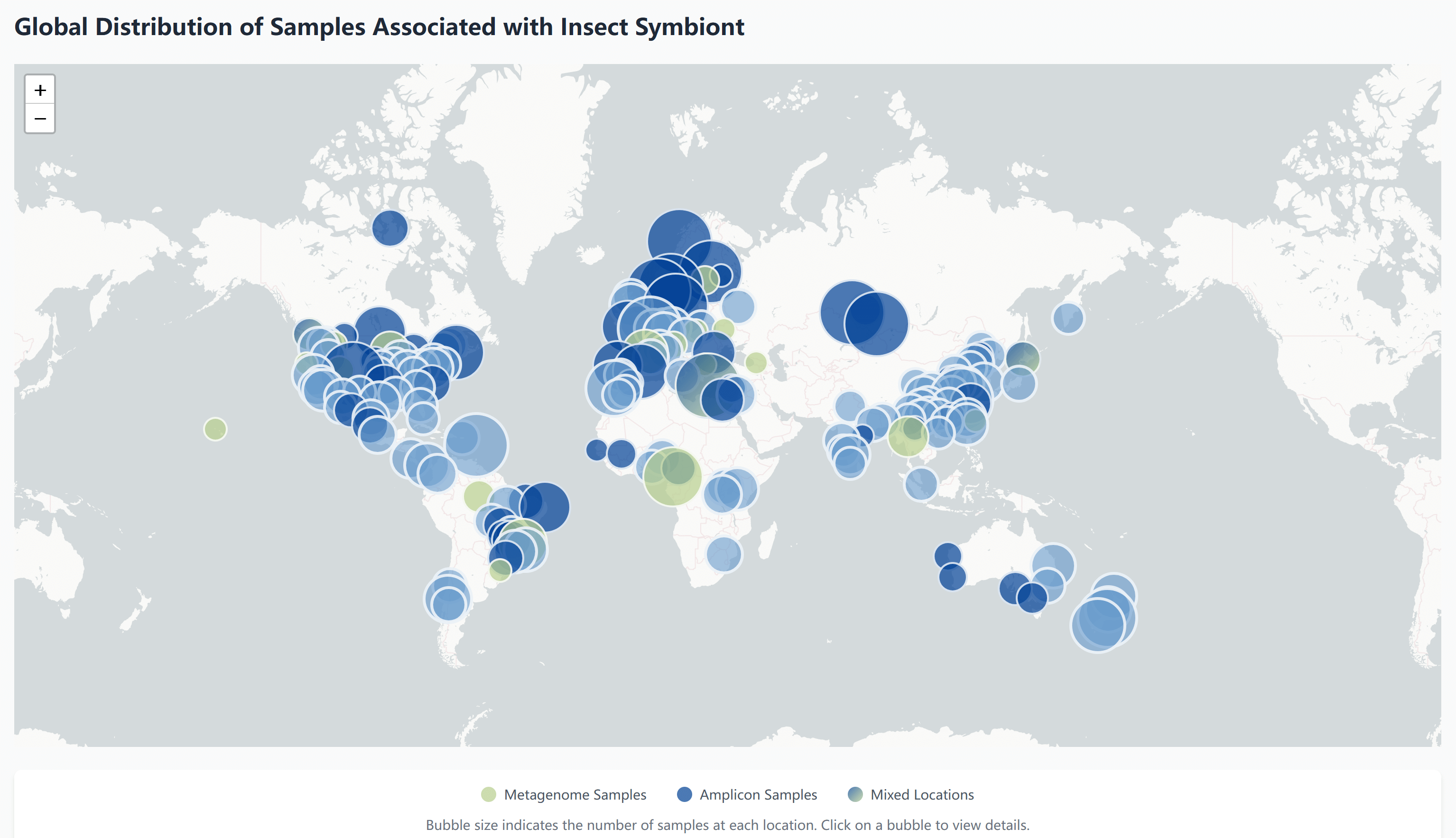
The interactive map offers several key features to help you explore sample distributions:
Hover Information
Hover over any bubble on the map to view detailed information about the sample:
- Sample data type (Amplicon/Metagenome)
- Precise geographical coordinates
- Host species information
Zoom Control
Use mouse scroll wheel to zoom in/out on the map:
- Zoom in to explore densely sampled areas
- View detailed distribution of nearby samples
- Zoom out for a global perspective
Sample Details
- Visit the Amplicon page for amplicon sequencing data
- Check the Metagenome page for metagenomic data
4. Taxonomic Composition Compare
The Composition Compare tool allows you to analyze and visualize taxonomic composition across different samples, helping you understand microbial community patterns and differences.
Tool Overview

The interface consists of four main sections:
- Database Sample Selection: Browse and select samples from our database
- Custom Data Upload: Upload your own taxonomic composition data
- Selected Samples: View and manage your selected samples
- Visualization Parameters: Configure the visualization settings
Quick Tips
- You can combine database samples with your custom data
- Selected samples are displayed in a two-column layout for easy management
- Use the Format Guide for proper data preparation
Data Input Methods
1. Database Sample Selection
Select samples from our database:
- Choose between Metagenome or Amplicon data types
- Filter samples by host species
- Select multiple samples using Ctrl/Cmd key
- Add selected samples to your analysis
Example Operation
- Select "Metagenome" from the data type dropdown
- Type host name in the filter box (e.g., "Apis")
- Hold Ctrl/Cmd and click to select multiple samples
- Click "Add Selected Samples" to include them
2. Custom Data Upload
Upload your own taxonomic composition data:
- Supports Kraken and Krona formats
- Download template files for reference
- Drag and drop or click to upload
- Check format guide for detailed requirements
File Format Notes
- Kraken format: Tab-separated with percentage and taxonomic info
- Krona format: Tab-separated with counts and full taxonomy path
- Maximum file size: 10MB
- Encoding: UTF-8 recommended
Visualization Configuration
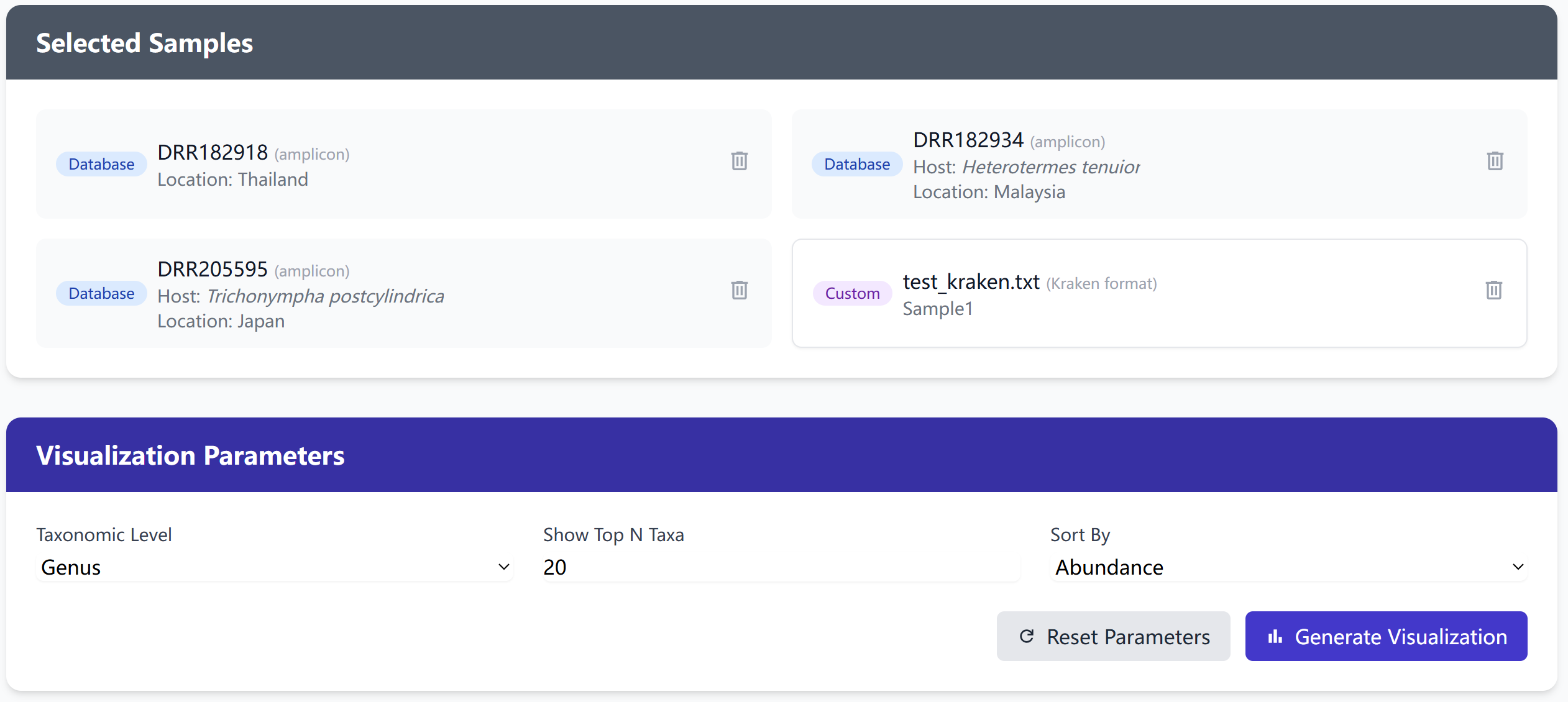
Customize your visualization with these parameters:
- Taxonomic Level: Select the taxonomic level for comparison (Phylum to Species)
- Top N Taxa: Choose how many top abundant taxa to display (1-20)
- Sort By: Order taxa by abundance or name
- Chart Type: Stacked bar chart showing relative abundances
Parameter Recommendations
- Start with Phylum level for a broad overview
- Use Top 10 taxa for clearer visualization
- Sort by abundance to highlight dominant taxa
- Adjust parameters to focus on your interests
Results and Export Options
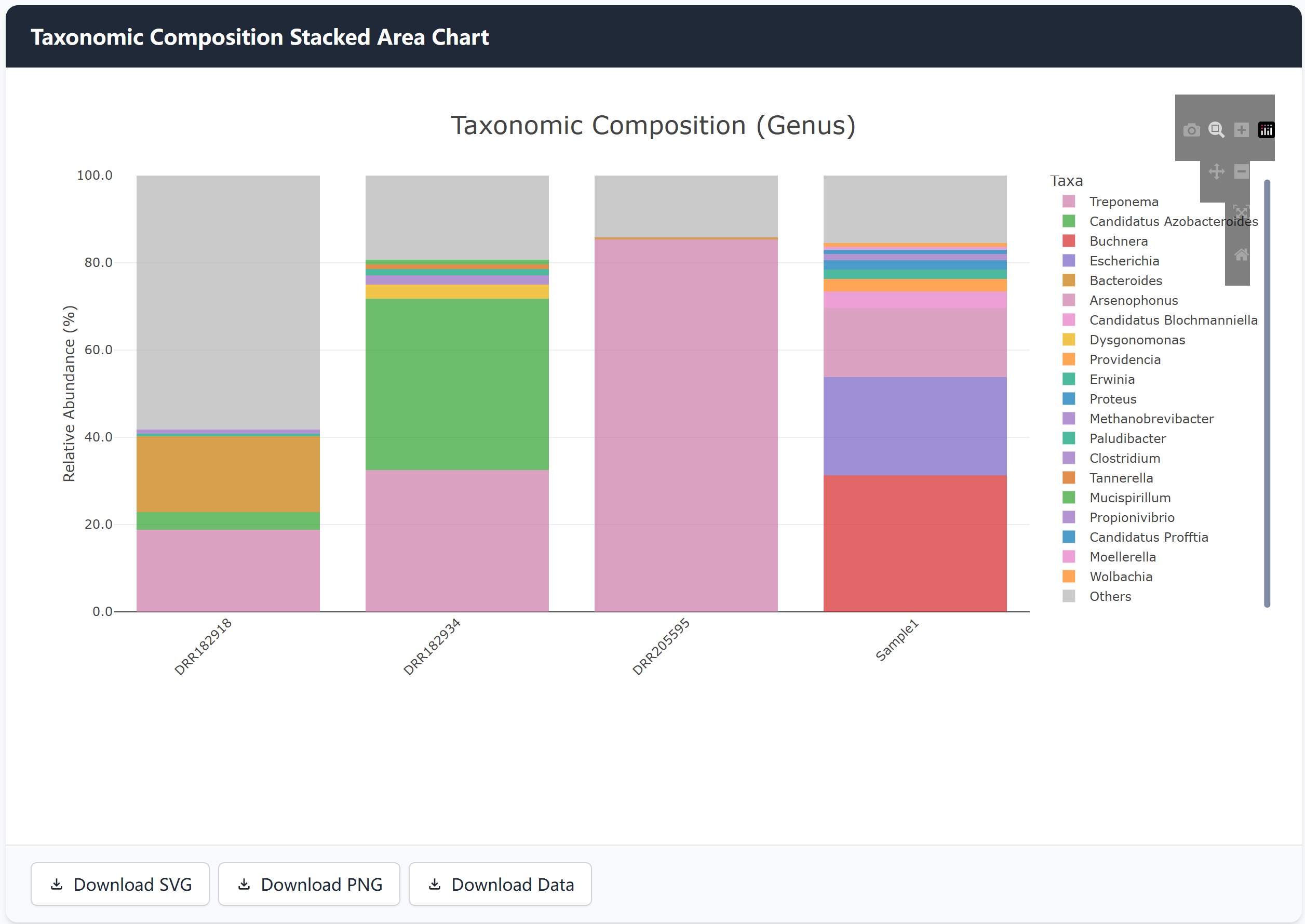
After generating the visualization:
- Interactive Chart: Hover over bars to see detailed values
- Download Options:
- SVG format for vector graphics
- PNG format for images
- CSV format for raw data
- Chart Customization: Use the toolbar for zooming, panning, and other interactions
Interactive Features
Mouse Controls
- Hover: View detailed values
- Click legend: Toggle taxa
- Double click: Reset view
Toolbar Options
- Zoom: Magnify areas
- Pan: Move chart view
- Reset: Restore default
Network Analysis
We built the network of symbionts (genera) with certain functions and their insects (species) based on their symbiosis relationships from literatures.
Quick Tip
The network visualization helps you understand the complex relationships between insects and their symbionts, revealing patterns of host-symbiont associations and functional distributions.
Network Visualization
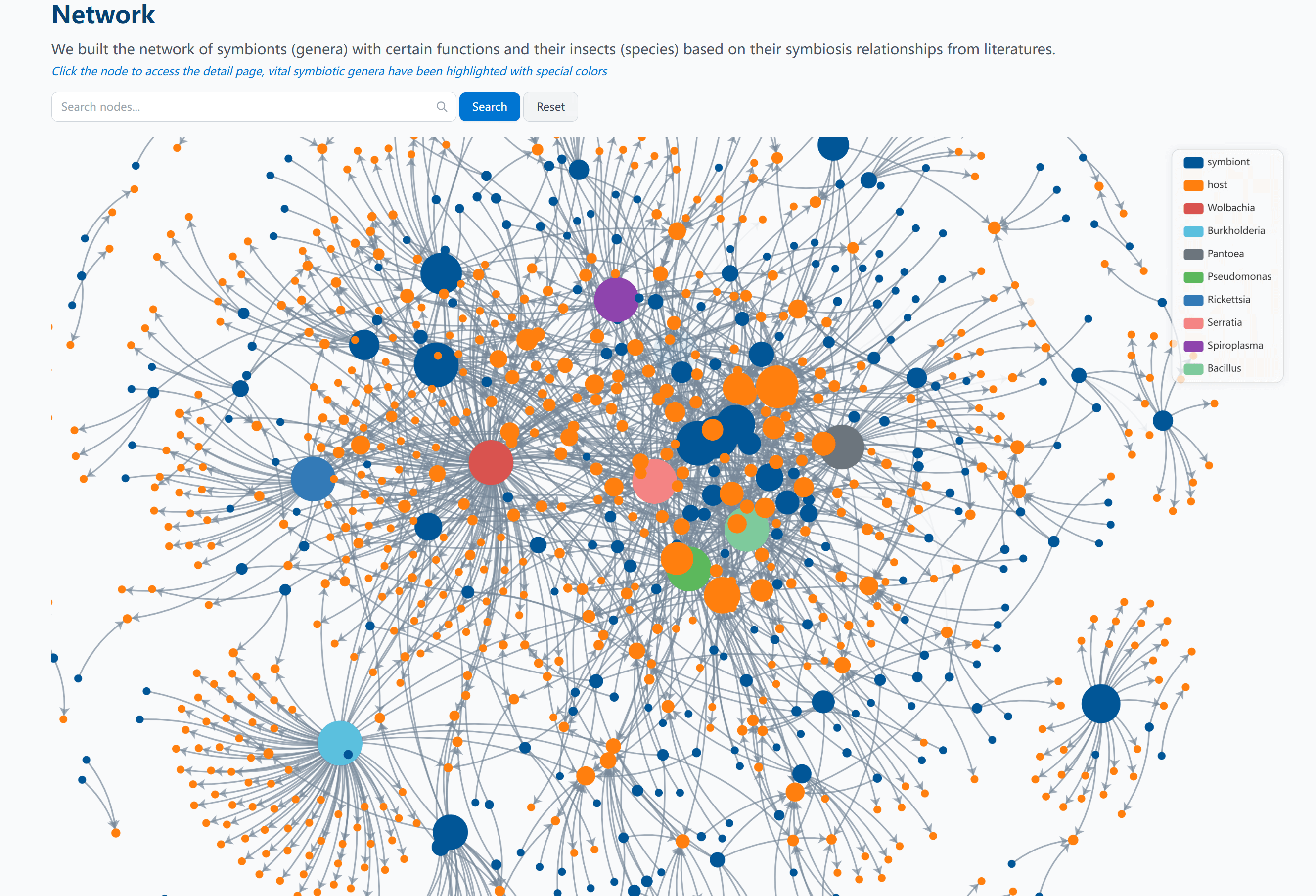
The network visualization provides several key features:
- Node Types:
- Orange circular nodes represent insect hosts (species level)
- Blue circular nodes represent symbionts (genus level)
Note: Vital symbiont genera have been highlighted with special colors
- Edge Connections: Lines between nodes represent documented symbiotic relationships from literature
Interactive Features
Node Hover Interaction
Hover over any node to highlight its direct connections, making it easier to focus on specific relationships:
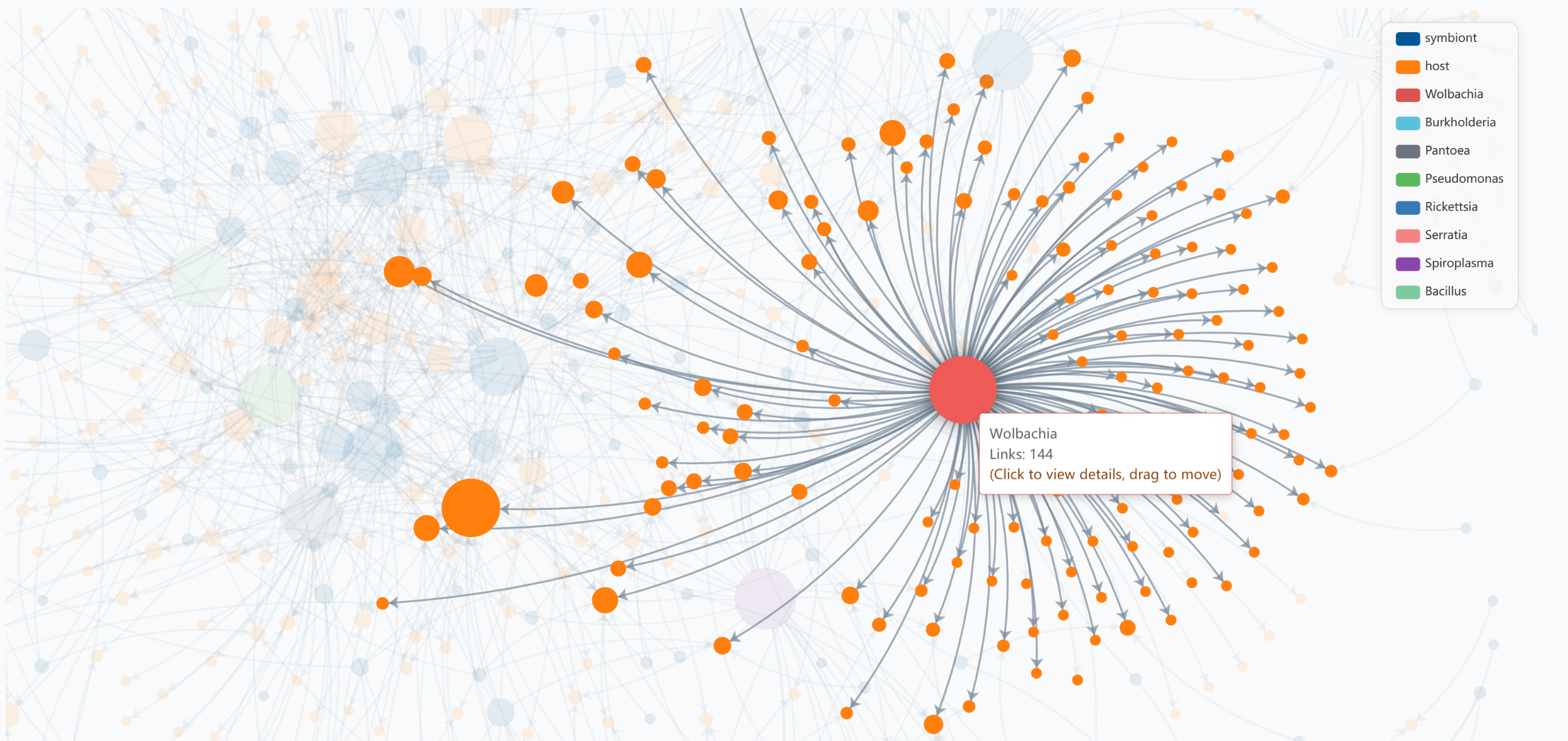
Example: Hovering over Wolbachia highlights its connections to various insect hosts
Link Hover Interaction
Hover over any connection line to emphasize the specific relationship between a symbiont and its host. Click the link to view the detailed symbiosis record:
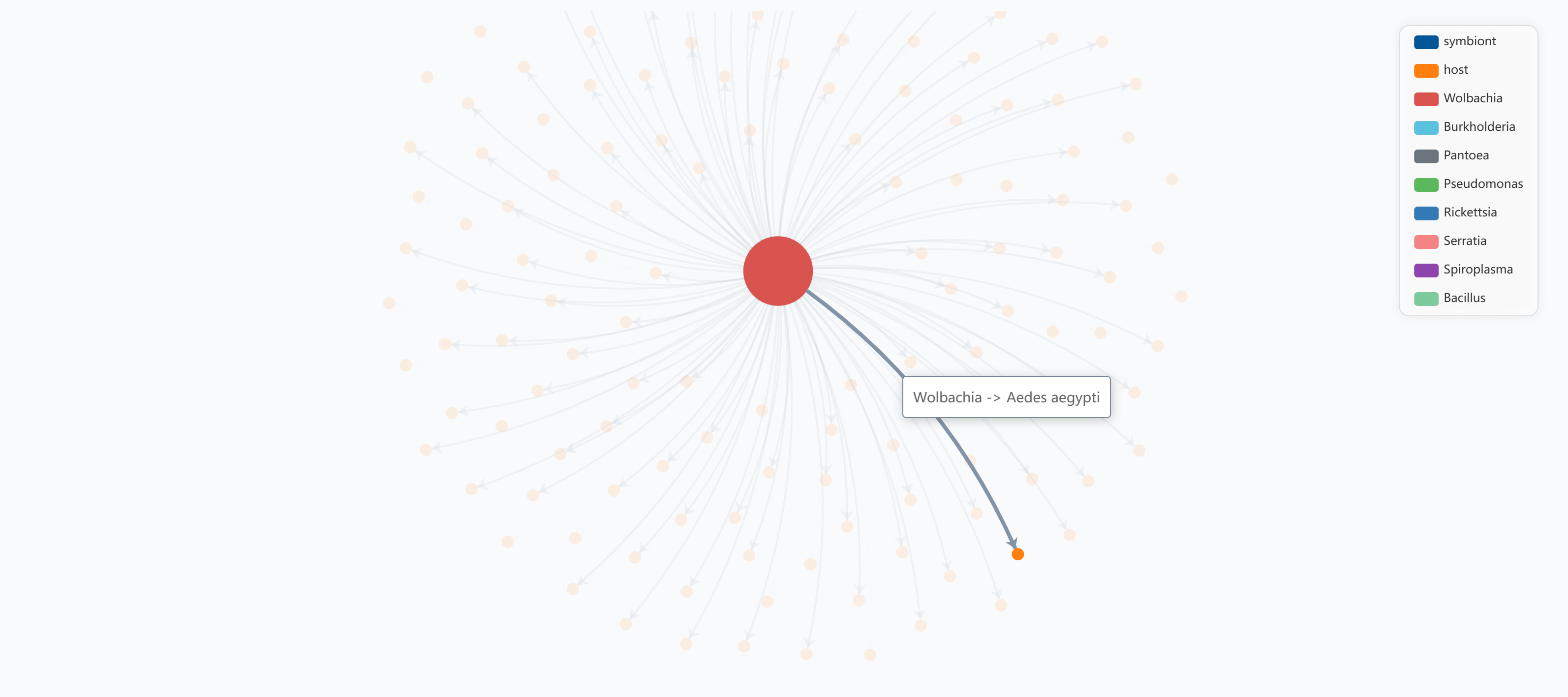
Example: Hovering over a connection highlights the specific symbiont-host relationship
Node Click Interaction
The network provides several click-based interactions:
- Click on nodes to maintain the highlight state of their connections
- Click symbiont nodes (blue) to view detailed symbiont information
- Click host nodes (orange) to view detailed host information
- Drag nodes to customize the network layout for better visualization
Search and Filter
Network Search
Given the complexity of the network, we provide a powerful search function to help you locate specific nodes and their relationships. When you search for a node, it will be highlighted with a golden glow to make it stand out:
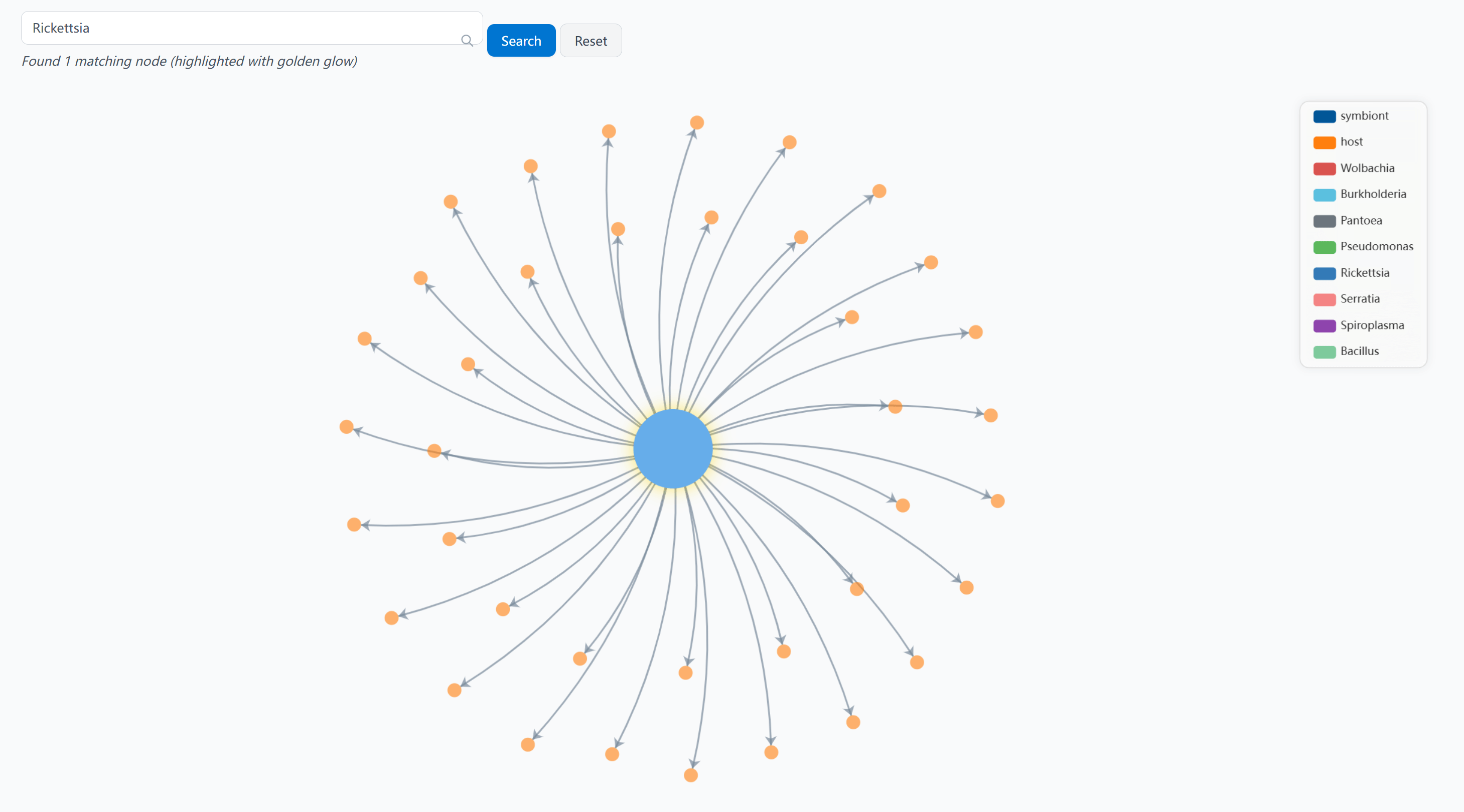
Example: Searching for "Rickettsia" highlights the node and its connections in the network
Search Tips
- Search is case-insensitive for your convenience
- Partial matches are supported to help you find related nodes
- Results update in real-time as you type
Network Filter
Our filtering system allows you to focus on specific symbiont-host relationships by selecting nodes from the right panel. This helps you visualize exactly the relationships you're interested in:
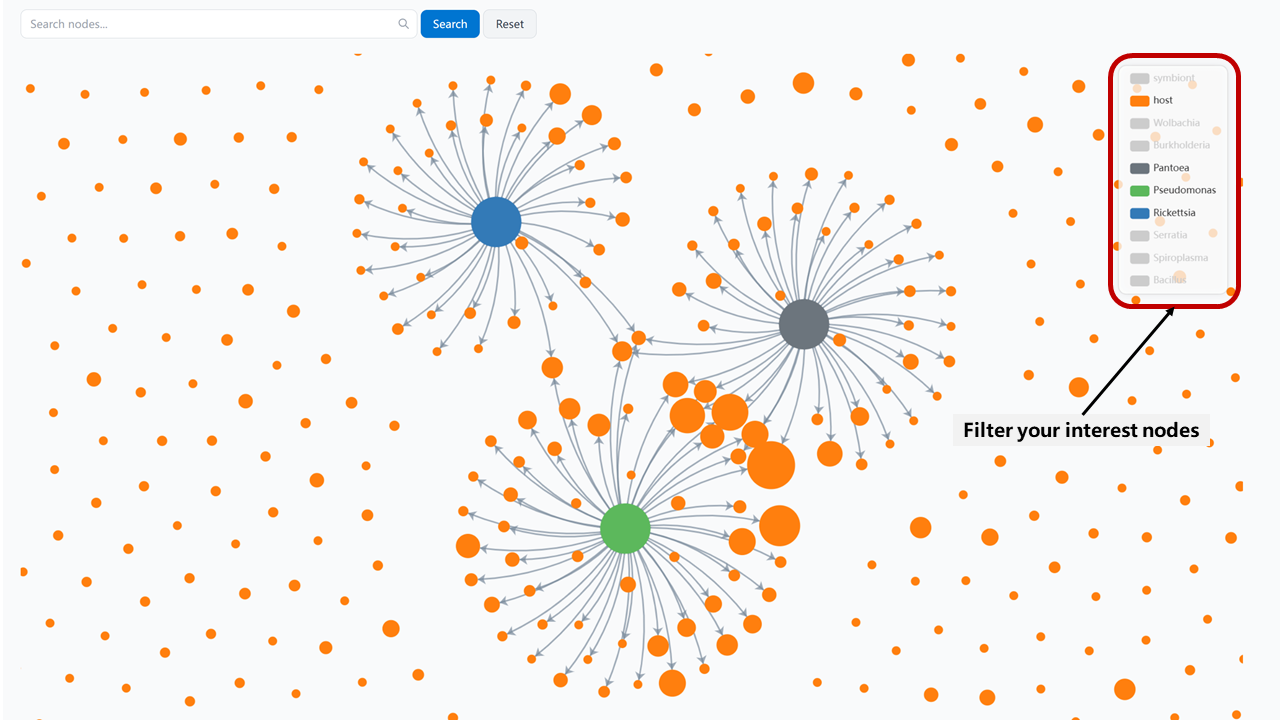
Example: Filtering the network to show specific symbiont-host relationships
The filter panel provides several options:
- Host Filters: Filter by insect orders or specific host species
- Symbiont Filters: Filter by symbiont genera or specific functions
- Relationship Filters: Focus on specific types of symbiotic relationships
Multiple filters can be combined to create more specific views of the network, helping you focus on exactly the relationships you want to explore.
iSymSeek Guide
iSymSeek interface showing the chat window and example interactions
iSymSeek is an AI-powered assistant designed to help you explore and understand insect symbiont relationships. It combines natural language processing with our comprehensive database to provide intelligent, context-aware responses to your queries.
Key Features
- Natural language interaction for database queries
- Comprehensive knowledge about insect symbionts
- Context-aware responses with database integration
- Real-time assistance for database navigation
How to Use iSymSeek
Types of Questions You Can Ask
Database Questions
- "How do I search for specific symbiont records?"
- "What tools are available for analyzing metagenome data?"
- "How can I download sequence data from the database?"
Scientific Queries
- "What are the known functions of Wolbachia in insects?"
- "Which symbionts are commonly found in honeybees?"
- "How do bacterial symbionts affect insect reproduction?"
Analysis Help
- "How do I interpret the network visualization?"
- "What do the different scores mean in batch annotation results?"
- "Can you explain the taxonomic composition chart?"
Best Practices
Do's
- Ask specific, focused questions
- Provide context when needed
- Use clear, simple language
- Follow up for clarification
Don'ts
- Ask multiple questions at once
- Use vague or ambiguous terms
- Expect real-time data updates
- Share sensitive information
Limitations and Considerations
Context Limitations
Conversations are limited to 5 messages. Start a new session for new topics.
Information Accuracy
Always verify critical information against the database content.
Data Currency
Responses are based on the latest database update, not real-time data.
Tips and Examples
Example Conversations
Database Navigation
User: "How can I find all symbionts associated with honeybees?"
iSymSeek: "You can find honeybee symbionts by: 1. Going to the 'Browse' section 2. Selecting 'Host Species' 3. Searching for 'Apis mellifera' 4. Viewing the associated symbiont records"
Scientific Information
User: "How does Wolbachia influence the reproductive system of Drosophila melanogaster?"
iSymSeek: "Wolbachia, a genus of intracellular bacteria, is well-known for its ability to manipulate the reproductive systems of its insect hosts, including Drosophila melanogaster. Here's how Wolbachia influences the reproductive system of this model organism: 1. Cytoplasmic Incompatibility (CI): Mechanism: Wolbachia induces cytoplasmic incompatibility, a phenomenon where the sperm of infected males is incompatible with the eggs of uninfected females. This results in embryonic lethality or reduced fertility. Outcome: Infected females can successfully mate with both infected and uninfected males, giving them a reproductive advantage. This promotes the spread of Wolbachia through host populations. 2. Feminization: In some cases, Wolbachia can convert genetic males into functional females by interfering with sex determination pathways. However, this effect is less common in Drosophila melanogaster compared to other insect species. 3. Parthenogenesis Induction: While not typically observed in Drosophila melanogaster, Wolbachia can induce parthenogenesis (reproduction without fertilization) in some other insects. This allows females to produce offspring without mating. 4. Male Killing: In certain hosts, Wolbachia selectively kills male embryos, increasing the proportion of female offspring. Although rare in Drosophila melanogaster, this strategy enhances the transmission of Wolbachia through female hosts. Ecological and Evolutionary Implications: The manipulation of host reproduction by Wolbachia has significant ecological and evolutionary consequences: - It can drive rapid changes in host population dynamics. - It may influence speciation processes by creating reproductive barriers between infected and uninfected populations. - It has been leveraged in biocontrol strategies to reduce populations of disease vectors like mosquitoes. Database Advice: To explore more about Wolbachia-host interactions or specific strains affecting Drosophila melanogaster, you can use iSymBase's Symbiont module to search for relevant data on symbiont-host relationships and their biological effects. Let me know if you'd like further details or assistance navigating iSymBase!"
Tool Usage
User: "How do I use the batch annotation tool?"
iSymSeek: "The batch annotation tool allows you to:
1. Upload taxonomic composition data (Kraken, MetaPhlAn, or Krona formats)
2. Select your file format from the dropdown menu
3. Specify host information (insect order and species name)
4. Get potential symbiont matches with scoring
After clicking "Search Symbionts," you'll see a table of results showing potential symbionts, their functions, abundance
percentages, and match scores. You can download the complete results for further analysis."
💡 Quick Tips for Better Results
- Start with broad questions and narrow down based on responses
- Use scientific names when possible for more accurate results
- Ask for clarification if you don't understand something
- Refresh the page to start a new conversation about a different topic
Frequently Asked Questions
Find answers to common questions about iSymBase and its features. Can't find what you're looking for? Contact our support team.
All symbiont records in our database come exclusively from peer-reviewed scientific literature. The functional descriptions are taken directly from the original publications, ensuring accuracy and fidelity to the source. Additionally, our classification criteria are based on a comprehensive review of all collected functional records combined with insights from relevant past reviews.
The Batch Anno Tool identifies potential symbionts by:
- Comparing your taxonomic data against our insect symbiont database
- Scoring matches based on multiple factors:
- Abundance percentage in your sample
- Taxonomic match level (species matches score higher than genus-only matches)
- Host insect match (same order +10 points, same species +20 points)
- Richness of functional description (more detailed descriptions score higher)
The system then ranks potential symbionts by total score, helping you identify the most likely symbiotic relationships in your data.
You can find all symbionts of specific host by:
- Going to the 'Browse' section on the top navigation
- Selecting 'Host Species'
- Searching for 'Apis mellifera' (the host latin name)
- Viewing the associated symbiont records
To find specific relationships:
-
Use the search box to locate specific hosts or symbionts
- Type a name and press Enter or click "Search"
- Matching nodes will be highlighted and their connections preserved
-
Click on connections (edges) between nodes to:
- View the specific symbiotic relationship details
- Open a filtered search page showing all records of that relationship
-
Click on nodes to access detailed information pages about:
- Host species (orange nodes)
- Symbiont genera (blue nodes)
The genome catalog consists of 3,520 newly recovered MAGs (Metagenome-Assembled Genomes) and 2,078 published insect symbiont genomes from sources like NCBI, NGDC, and BV-BRC. These genomes were processed as follows:
1. Quality Assessment
- Each genome was evaluated using CheckM
- The MIMAG standard was applied, with genomes removed if they had:
- Completeness <50%
- Contamination >10%
- Quality score (QS) <50 (QS = completeness - 5 × contamination)
2. Taxonomic Annotation
- GTDB-Tk was used for classification under default parameters (dataset r220)
- Additional taxonomic and functional information from literature was incorporated
The gene catalog was built from predicted genes in the genomes using the following steps:
1. Gene Prediction
- Prodigal was used to predict genes:
- Metagenomic contigs processed in metagenomic mode (-p meta)
- Single genomes processed in single-genome mode (-p single)
2. Nonredundant Gene Clustering
- CD-HIT was used to remove redundant genes, grouping sequences with:
- ≥90% identity
- ≥90% coverage
- This resulted in a nonredundant gene catalog for each host species
3. Functional Annotation
- DIAMOND aligned genes to the NR (non-redundant protein) database to determine functions
- eggNOG-mapper assigned:
- COG functional categories
- KEGG pathways using eggNOG DB 5.0.2
We're Here to Help!
Our FAQ section is continuously updated based on user feedback and common questions. Can't find what you're looking for? Have suggestions for improvement?