Agrotis ipsilon
dark sword-grass, black cutworm, greasy cutworm, floodplain cutworm or ipsilon dart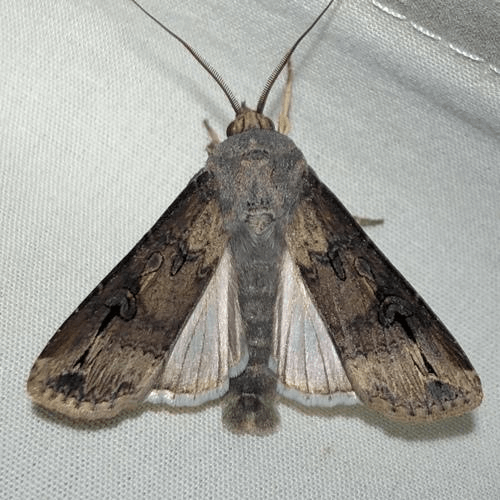
Agrotis ipsilon is a small noctuid moth found worldwide. The moth gets its scientific name from black markings on its forewings shaped like the letter Y or the Greek letter upsilon. The larvae are known as cutworms because they cut plants and other crops. The larvae are serious agricultural pests and feed on nearly all varieties of vegetables and many important grains.
Host Genome
Scaffold| Genome ID | Level | BUSCO Assessment |
|---|---|---|
| GCA_004193855.1 | Scaffold |
C:97.9%[S:97.1%,D:0.8%],F:0.5%,M:1.6%,n:1367
|
Download Genome Files
Related Symbionts
7 recordsSymbiont records associated with Agrotis ipsilon
| Classification | Function | Function Tags | Reference | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Bacteria
|
Gut bacterial communities (Amplicon data) in Agrotis ipsilon larvae are capable of degrading various polysaccharides (including cellulose, xylan, pec… |
cellulose hydrolysis
carbohydrate metabolism
|
||
|
Aspergillus parasiticus
Ascomycota |
Fungi
|
Aspergillus parasiticus (from oral secretions) induced higher defense responses in plants mediated by the insect Agrotis ipsilon. |
plant defense modulation
|
|
|
Fusarium subglutinans
Ascomycota |
Fungi
|
Fusarium subglutinans (from oral secretions) induced higher defense responses in plants mediated by the insect Agrotis ipsilon. |
plant defense modulation
|
|
|
Fusarium lusitanicus
Ascomycota |
Fungi
|
Fusarium lusitanicus (from oral secretions) induced higher defense responses in plants mediated by the insect Agrotis ipsilon. |
plant defense modulation
|
|
|
Mucor circinelloides
Mucoromycota |
Fungi
|
Mucor circinelloides (from oral secretions) induced higher defense responses in plants mediated by the insect Agrotis ipsilon. |
plant defense modulation
|
|
|
Geotrichum candidum
Ascomycota |
Fungi
|
Geotrichum candidum (from oral secretions) induced higher defense responses in plants mediated by the insect Agrotis ipsilon. |
plant defense modulation
|
|
|
Aspergillus niger
Ascomycota |
Fungi
|
Aspergillus niger (from oral secretions) induced higher defense responses in plants mediated by the insect Agrotis ipsilon. |
plant defense modulation
|
Metagenome Information
0 recordsMetagenome sequencing data associated with Agrotis ipsilon
| Run | Platform | Location | Date | BioProject |
|---|---|---|---|---|
No metagenomes foundNo metagenome records associated with this host species. |
||||
Amplicon Information
0 recordsAmplicon sequencing data associated with Agrotis ipsilon
| Run | Classification | Platform | Location | Environment |
|---|---|---|---|---|
No amplicons foundNo amplicon records associated with this host species. |
||||
Related Articles
2 recordsResearch articles related to Agrotis ipsilon
| Title | Authors | Journal | Year | DOI |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Elkraly, OA; Awad, M; El-Saadany, HM ... Abd Elrahman, T; Elnagdy, SM
|
Animal Microbiome
|
2023
|
10.1186/s42523-023-00264-6 | |
|
Chen, XW; Peiffer, M; Tan, CW; Felton, GW
|
Arthropod-Plant Interactions
|
2020
|
10.1007/s11829-020-09767-4 |